Selection Sort – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
**Selection sort** is a simple and efficient sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly selecting the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion of the list and moving it to the sorted portion of the list.
The algorithm repeatedly selects the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion of the list and swaps it with the first element of the unsorted part. This process is repeated for the remaining unsorted portion until the entire list is sorted.
How does Selection Sort Algorithm work?
Lets consider the following array as an example: **arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11}**
**First pass:**
- For the first position in the sorted array, the whole array is traversed from index 0 to 4 sequentially. The first position where **64** is stored presently, after traversing whole array it is clear that **11** is the lowest value.
- Thus, replace 64 with 11. After one iteration **11**, which happens to be the least value in the array, tends to appear in the first position of the sorted list.
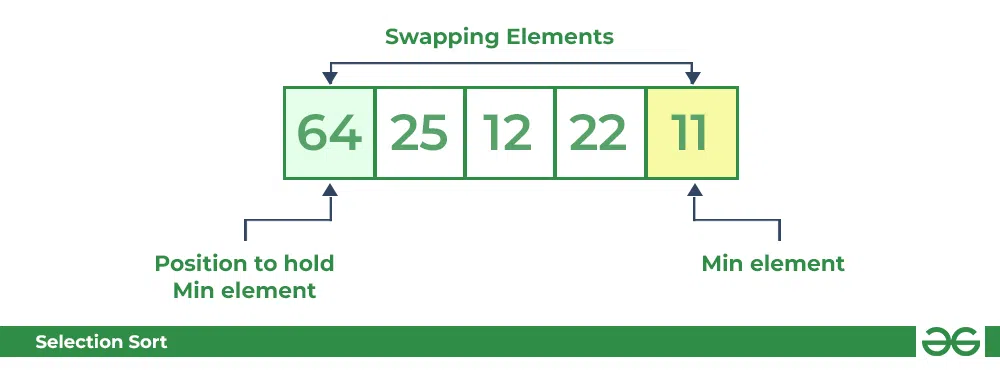Selection Sort Algorithm Swapping 1st element with the minimum in array **Second Pass:**
- For the second position, where 25 is present, again traverse the rest of the array in a sequential manner.
- After traversing, we found that **12** is the second lowest value in the array and it should appear at the second place in the array, thus swap these values.
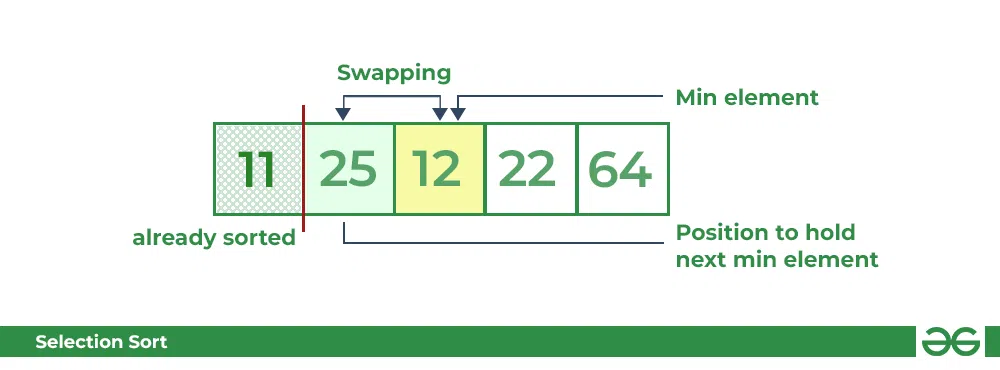Selection Sort Algorithm swapping i=1 with the next minimum element **Third Pass:**
- Now, for third place, where **25** is present again traverse the rest of the array and find the third least value present in the array.
- While traversing, **22** came out to be the third least value and it should appear at the third place in the array, thus swap **22** with element present at third position.
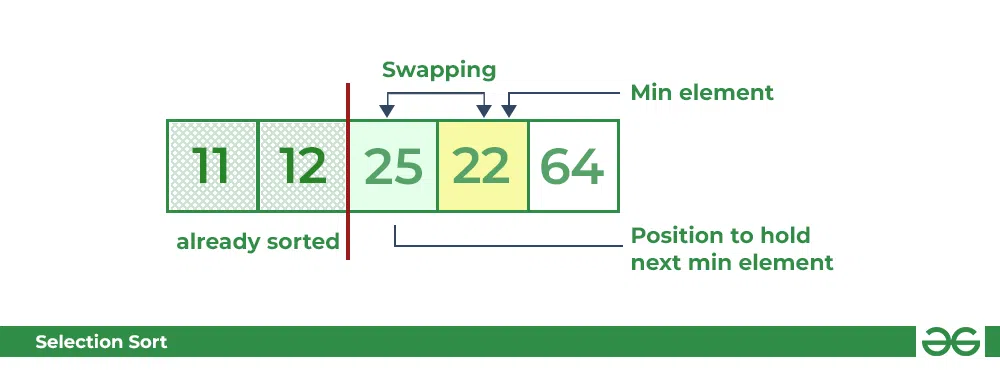Selection Sort Algorithm swapping i=2 with the next minimum element **Fourth pass:**
- Similarly, for fourth position traverse the rest of the array and find the fourth least element in the array
- As **25** is the 4th lowest value hence, it will place at the fourth position.
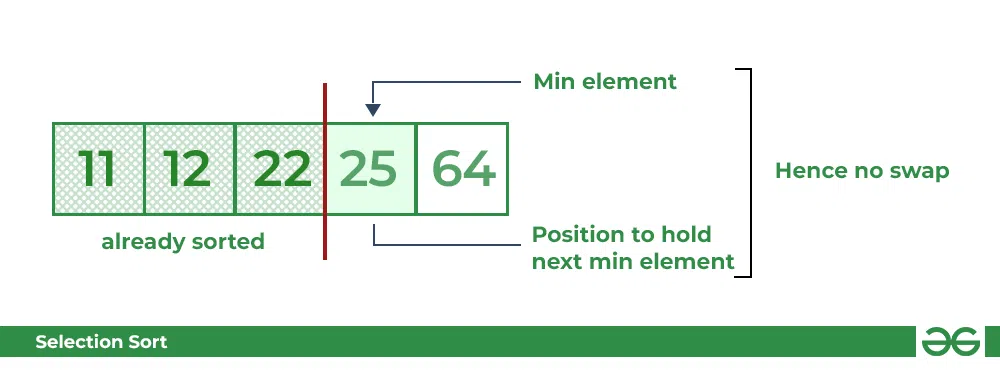Selection Sort Algorithm swapping i=3 with the next minimum element **Fifth Pass:**
- At last the largest value present in the array automatically get placed at the last position in the array
- The resulted array is the sorted array.
Selection Sort Algorithm Required sorted array
Recommended PracticeSelection SortTry It! Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
// C++ program for implementation of
// selection sort
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
// Function for Selection sort
void selectionSort(int arr[], int n)
{
int i, j, min_idx;
// One by one move boundary of
// unsorted subarray
for (i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
// Find the minimum element in
// unsorted array
min_idx = i;
for (j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx])
min_idx = j;
}
// Swap the found minimum element
// with the first element
if (min_idx != i)
swap(arr[min_idx], arr[i]);
}
}
// Function to print an array
void printArray(int arr[], int size)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// Driver program
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 64, 25, 12, 22, 11 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function Call
selectionSort(arr, n);
cout << "Sorted array: \n";
printArray(arr, n);
return 0;
}
// This is code is contributed by rathbhupendra
C
Java
Python3
C#
Javascript
PHP
Output
Sorted array:
11 12 22 25 64
Complexity Analysis of Selection Sort ————————————-
**Time Complexity:** The time complexity of Selection Sort is **O(N**2**)** as there are two nested loops:
- One loop to select an element of Array one by one = O(N)
- Another loop to compare that element with every other Array element = O(N)
- Therefore overall complexity = O(N) * O(N) = O(N*N) = O(N2)
**Auxiliary Space:** O(1) as the only extra memory used is for temporary variables while swapping two values in Array. The selection sort never makes more than O(N) swaps and can be useful when memory writing is costly.
Advantages of Selection Sort Algorithm
- Simple and easy to understand.
- Works well with small datasets.
**Disadvantages of the Selection Sort Algorithm**
- Selection sort has a time complexity of O(n^2) in the worst and average case.
- Does not work well on large datasets.
- Does not preserve the relative order of items with equal keys which means it is not stable.
Frequently Asked Questions on Selection Sort
**Q1. Is Selection Sort Algorithm stable?**
The default implementation of the Selection Sort Algorithm is **not stable**. However, it can be made stable. Please see the stable Selection Sort for details.
**Q2. Is Selection Sort Algorithm in-place?**
Yes, Selection Sort Algorithm is an in-place algorithm, as it does not require extra space.