Introduction to Linked List – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
**Linked List** is basically **chains of nodes** where each node contains information such as **data** and a **pointer to the next node** in the chain. It is a popular data structure with a wide range of real-world applications. In this article, we will provide a complete introduction of Linked List, which will help you tackle any problem based on Linked List.
Table of Content
- What is a Linked List?
- Basic Terminologies of Linked List
- Importance of Linked List
- Types of Linked List
- Singly Linked List
- Doubly Linked List
- Implementation of Linked List
- Linked List vs. Array
- Advantages of Linked List
- Disadvantages of Linked List
- Applications of Linked List
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Linked list What is a Linked List? ———————-
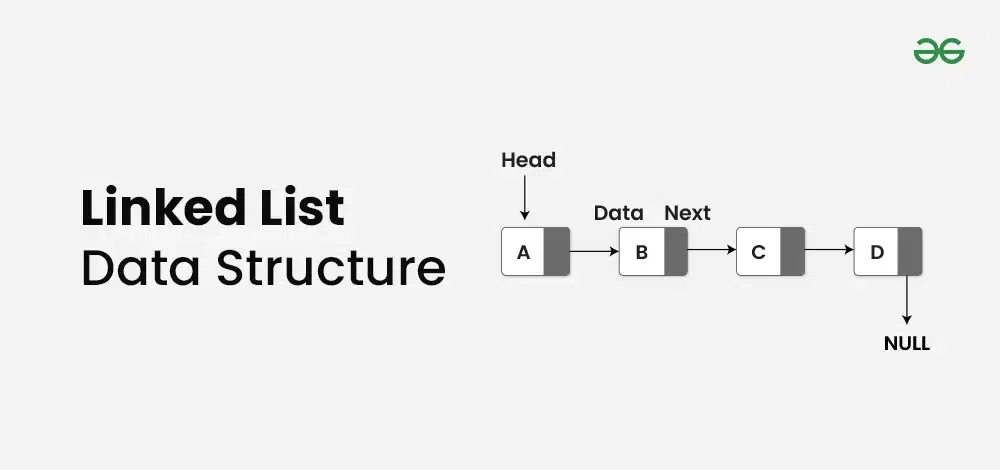
Linked List is a **linear data structure** which looks like a series of **nodes, where each node has two parts: **data** and **next pointer**. Unlike Arrays, Linked List elements are not stored at a contiguous location. In the linked list there is a **head pointer**, which points to the first element of the linked list, and if the list is empty then it simply points to null or nothing.
 Basic Terminologies of Linked List:
Basic Terminologies of Linked List:
- **Head:** The Head of a linked list is a pointer to the first node or reference of the first node of linked list. This pointer marks the beginning of the linked list.
- **Node:** Linked List consists of a series of nodes where each node has two parts: **data** and **next pointer**.
- **Data:** Data is the part of node which stores the information in the linked list.
- **Next pointer:** Next pointer is the part of the node which points to the next node of the linked list.
**Importance of Linked List:**
Here are a few advantages of a linked list that is listed below, it will help you understand why it is necessary to know.
- **Dynamic Data structure:** The size of memory can be allocated or de-allocated at run time based on the operation insertion or deletion.
- **Ease of Insertion/Deletion:** The insertion and deletion of elements are simpler than arrays since no elements need to be shifted after insertion and deletion, Just the address needed to be updated.
- **Efficient Memory Utilization:** As we know Linked List is a dynamic data structure the size increases or decreases as per the requirement so this avoids the wastage of memory.
- **Implementation:** Various advanced data structures can be implemented using a linked list like a stack, queue, graph, hash maps, etc.
**Types of Linked List:**
There are mainly three types of linked lists:
- **Singly linked list**
- **Doubly linked list**
- **Circular linked list**
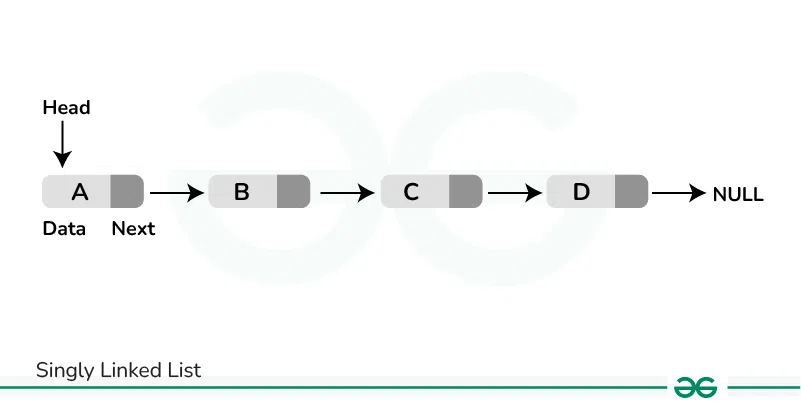
[**1. Singly Linked List](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/data-structures/linked-list/singly-linked-list/):**
**Singly Linked List** is a type of linked list where each node has two parts: **data** and **next pointer. The data part stores the information and the next pointer points to the next node of the linked list. The next pointer of the last node stores **null** as it is the last node of the linked list and there is no next node. Traversal of items can be done in the forward direction only due to the linking of every node to its next node.
 ——
Insertion in Linked List
========================
——
Insertion in Linked List
========================
Given a Linked List, the task is to insert a new node in this given Linked List at the following positions:
- At the front of the linked list
- After a given node.
- At the end of the linked list.
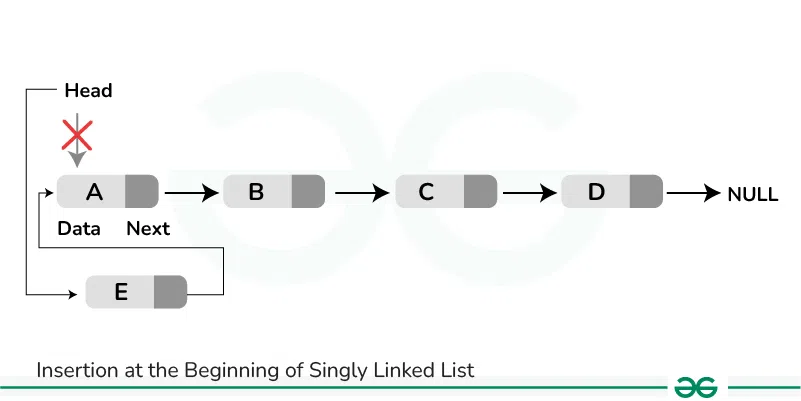
How to Insert a Node at the Front/Beginning of Linked List
**Approach:**
To insert a node at the start/beginning/front of a Linked List, we need to:
- Make the first node of Linked List linked to the new node
- Remove the head from the original first node of Linked List
- Make the new node as the Head of the Linked List.
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
| // Given a reference (pointer to pointer) // to the head of a list and an int, // inserts a new node on the front of // the list. void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { // 1. allocate node Node* new_node = new Node(); // 2. put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // 3. Make next of new node as head new_node->next = (*head_ref); // 4. Move the head to point to // the new node (*head_ref) = new_node; } |
| — |
C
| /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, inserts a new node on the front of the list. */ void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. Make next of new node as head */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* 4. move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } |
| — |
Java
| /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new Node at front of the list. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void push(int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } |
| — |
Python3
| # This function is in LinkedList class # Function to insert a new node at the beginning def push(self, new_data): # 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & # Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new Node as head new_node.next = self.head # 4. Move the head to point to new Node self.head = new_node |
| — |
C#
| /* Inserts a new Node at front of the list. */ public void push(int new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new Node at front of the list. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function push(new_data) { /* 1 & 2: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 3. Make next of new Node as head */ new_node.next = head; /* 4. Move the head to point to new Node */ head = new_node; } </script> |
| — |
**Complexity Analysis:**
- **Time Complexity:** O(1), We have a pointer to the head and we can directly attach a node and change the pointer. So the Time complexity of inserting a node at the head position is O(1) as it does a constant amount of work.
- **Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
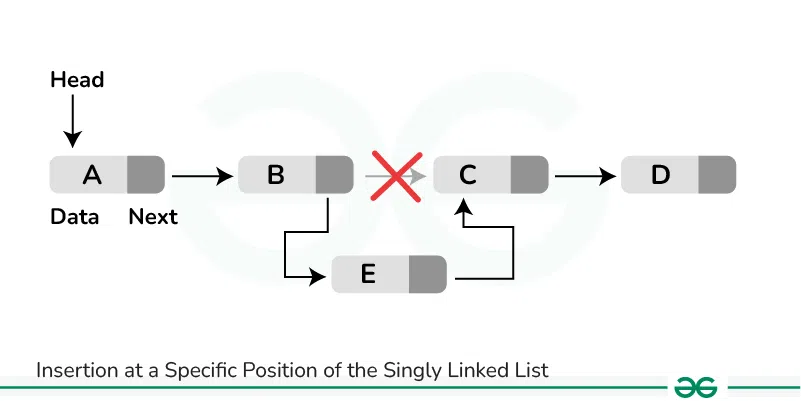
How to Insert a Node after a Given Node in Linked List
**Approach:**
To insert a node after a given node in a Linked List, we need to:
- Check if the given node exists or not.
- If it do not exists,
- terminate the process.
- If the given node exists,
- Make the element to be inserted as a new node
- Change the next pointer of given node to the new node
- Now shift the original next pointer of given node to the next pointer of new node
- If it do not exists,
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
| // Given a node prev_node, insert a // new node after the given // prev_node void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data) { // 1. Check if the given prev_node is NULL if (prev_node == NULL) { cout << "The given previous node cannot be NULL"; return; } // 2. Allocate new node Node* new_node = new Node(); // 3. Put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // 4. Make next of new node as // next of prev_node new_node->next = prev_node->next; // 5. move the next of prev_node // as new_node prev_node->next = new_node; } |
| — |
C
| /* Given a node prev_node, insert a new node after the given prev_node */ void insertAfter(struct Node* prev_node, int new_data) { /*1. check if the given prev_node is NULL */ if (prev_node == NULL) { printf("the given previous node cannot be NULL"); return; } /* 2. allocate new node */ struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); /* 3. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 4. Make next of new node as next of prev_node */ new_node->next = prev_node->next; /* 5. move the next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node->next = new_node; } |
| — |
Java
| /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null) { System.out.println( "The given previous node cannot be null"); return; } /* 2. Allocate the Node & 3. Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } |
| — |
Python3
| # This function is in LinkedList class. # Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ def insertAfter(self, prev_node, new_data): # 1. check if the given prev_node exists if prev_node is None: print("The given previous node must inLinkedList.") return # 2. Create new node & # 3. Put in the data new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node new_node.next = prev_node.next # 5. make next of prev_node as new_node prev_node.next = new_node |
| — |
C#
| /* Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. */ public void insertAfter(Node prev_node, int new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null) { Console.WriteLine("The given previous node" + " cannot be null"); return; } /* 2 & 3: Allocate the Node & Put in the data*/ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> /* This function is in LinkedList class. Inserts a new node after the given prev_node. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function insertAfter(prev_node, new_data) { /* 1. Check if the given Node is null */ if (prev_node == null) { document.write("The given previous node cannot be null"); return; } /* 2. Allocate the Node & 3. Put in the data*/ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. Make next of new Node as next of prev_node */ new_node.next = prev_node.next; /* 5. make next of prev_node as new_node */ prev_node.next = new_node; } </script> |
| — |
**Complexity Analysis:**
- **Time complexity:** O(1), since prev_node is already given as argument in a method, no need to iterate over list to find prev_node
- **Auxiliary Space:** O(1) since using constant space to modify pointers
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
How to Insert a Node at the End of Linked List
**Approach:**
To insert a node at the end of a Linked List, we need to:
- Go to the last node of the Linked List
- Change the next pointer of last node from NULL to the new node
- Make the next pointer of new node as NULL to show the end of Linked List
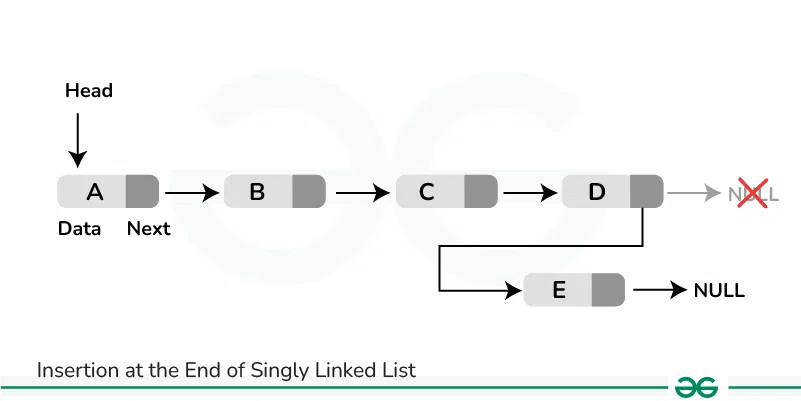
Below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
| // Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head // of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { // 1. allocate node Node* new_node = new Node(); // Used in step 5 Node* last = *head_ref; // 2. Put in the data new_node->data = new_data; // 3. This new node is going to be // the last node, so make next of // it as NULL new_node->next = NULL; // 4. If the Linked List is empty, // then make the new node as head if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return; } // 5. Else traverse till the last node while (last->next != NULL) { last = last->next; } // 6. Change the next of last node last->next = new_node; return; } |
| — |
C
| /* Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head of a list and an int, appends a new node at the end */ void append(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* 1. allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); struct Node* last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/ /* 2. put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as NULL*/ new_node->next = NULL; /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new * node as head */ if (*head_ref == NULL) { *head_ref = new_node; return; } /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ while (last->next != NULL) last = last->next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last->next = new_node; return; } |
| — |
Java
| /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append(int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null) { head = new Node(new_data); return; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return; } |
| — |
Python3
| # This function is defined in Linked List class # Appends a new node at the end. This method is # defined inside LinkedList class shown above def append(self, new_data): # 1. Create a new node # 2. Put in the data # 3. Set next as None new_node = Node(new_data) # 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the # new node as head if self.head is None: self.head = new_node return # 5. Else traverse till the last node last = self.head while (last.next): last = last.next # 6. Change the next of last node last.next = new_node |
| — |
C#
| /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ public void append(int new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ Node new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null) { head = new Node(new_data); return; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ Node last = head; while (last.next != null) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return; } |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> /* Appends a new node at the end. This method is defined inside LinkedList class shown above */ function append(new_data) { /* 1. Allocate the Node & 2. Put in the data 3. Set next as null */ var new_node = new Node(new_data); /* 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new node as head */ if (head == null) { head = new Node(new_data); return; } /* 4. This new node is going to be the last node, so make next of it as null */ new_node.next = null; /* 5. Else traverse till the last node */ var last = head; while (last.next != null) last = last.next; /* 6. Change the next of last node */ last.next = new_node; return; } </script> |
| — |
**Complexity Analysis:**
- **Time complexity:** O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the linked list. Since there is a loop from head to end, the function does O(n) work.
- This method can also be optimized to work in O(1) by keeping an extra pointer to the tail of the linked list/
- **Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
Refer this post for detailed implementation of the above approach.
Introduction to Circular Linked List
Search an element in a Linked List (Iterative and Recursive)
Deletion in Linked List =======================
We have discussed Linked List Introduction and Linked List Insertion in previous posts on a singly linked list.
Let us formulate the problem statement to understand the deletion process.
Delete from a Linked List:-
You can delete an element in a list from:
- Beginning
- End
- Middle
1) Delete from Beginning:
Point head to the next node i.e. second node
temp = head
head = head->next
Make sure to free unused memory
free(temp); or delete temp;
2) Delete from End:
Point head to the previous element i.e. last second element
Change next pointer to null
struct node *end = head;
struct node *prev = NULL;
while(end->next)
{
prev = end;
end = end->next;
}
prev->next = NULL;
Make sure to free unused memory
free(end); or delete end;
3) Delete from Middle:
Keeps track of pointer before node to delete and pointer to node to delete
temp = head;
prev = head;
for(int i = 0; i < position; i++)
{
if(i == 0 && position == 1)
head = head->next;
free(temp)
else
{
if (i == position - 1 && temp)
{
prev->next = temp->next;
free(temp);
}
else
{
prev = temp;
if(prev == NULL) // position was greater than number of nodes in the list
break;
temp = temp->next;
}
}
}
Iterative Method to delete an element from the linked list:
To delete a node from the linked list, we need to do the following steps:
- Find the previous node of the node to be deleted.
- Change the next of the previous node.
- Free memory for the node to be deleted.
Below is the implementation to delete a node from the list at some position:
C++
| #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int number; Node* next; }; void Push(Node** head, int A) { Node* n = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); n->number = A; n->next = *head; *head = n; } void deleteN(Node** head, int position) { Node* temp; Node* prev; temp = *head; prev = *head; for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) { if (i == 0 && position == 1) { *head = (*head)->next; free(temp); } else { if (i == position - 1 && temp) { prev->next = temp->next; free(temp); } else { prev = temp; // Position was greater than // number of nodes in the list if (prev == NULL) break; temp = temp->next; } } } } void printList(Node* head) { while (head) { if (head->next == NULL) cout << "[" << head->number << "] " << "[" << head << "]->" << "(nil)" << endl; else cout << "[" << head->number << "] " << "[" << head << "]->" << head->next << endl; head = head->next; } cout << endl << endl; } // Driver code int main() { Node* list = (Node*)malloc(sizeof(Node)); list->next = NULL; Push(&list, 1); Push(&list, 2); Push(&list, 3); printList(list); // Delete any position from list deleteN(&list, 1); printList(list); return 0; } |
| — |
C
| // C code to delete a node from linked list #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> typedef struct Node { int number; struct Node* next; } Node; void Push(Node** head, int A) { Node* n = malloc(sizeof(Node)); n->number = A; n->next = *head; *head = n; } void deleteN(Node** head, int position) { Node* temp; Node* prev; temp = *head; prev = *head; for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) { if (i == 0 && position == 1) { *head = (*head)->next; free(temp); } else { if (i == position - 1 && temp) { prev->next = temp->next; free(temp); } else { prev = temp; // Position was greater than // number of nodes in the list if (prev == NULL) break; temp = temp->next; } } } } void printList(Node* head) { while (head) { printf("[%i] [%p]->%p\n", head->number, head, head->next); head = head->next; } printf("\n\n"); } // Drivers code int main() { Node* list = malloc(sizeof(Node)); list->next = NULL; Push(&list, 1); Push(&list, 2); Push(&list, 3); printList(list); // Delete any position from list deleteN(&list, 1); printList(list); return 0; } |
| — |
Java
| class Node { int number; Node next; } class Main { // This method adds a new node with a value A to the front of the linked list public static Node push(Node head, int A) { Node n = new Node(); // Create a new node n.number = A; // Assign the value A to the node n.next = head; // Set the next node of the new node to be the current head head = n; // Set the new node as the head of the linked list return head; // Return the new head of the linked list } // This method deletes the node at the given position from the linked list public static Node deleteN(Node head, int position) { Node temp = head; // Create a temporary node pointing to the head of the linked list Node prev = head; // Create a previous node pointing to the head of the linked list for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) { // Loop through the linked list to find the node at the given position if (i == 0 && position == 1) { // If the node to delete is the head head = head.next; // Set the next node as the new head } else { if (i == position - 1 && temp != null) { // If the node to delete is found prev.next = temp.next; // Set the next node of the previous node to be the next node of the current node } else { prev = temp; // Move the previous node to the current node // If the previous node is null, the position was greater than the number of nodes in the list if (prev == null) break; temp = temp.next; // Move the temporary node to the next node } } } return head; // Return the new head of the linked list } // This method prints the linked list public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { // Loop through the linked list if (head.next == null) { // If the current node is the last node System.out.println("[" + head.number + "] [" + head + "]->" + "(null)"); // Print the node value and null } else { System.out.println("[" + head.number + "] [" + head + "]->" + head.next); // Print the node value and the next node } head = head.next; // Move to the next node } System.out.println(); System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { Node list = new Node(); // Create a new linked list list.next = null; // Set the next node of the first node to be null list = push(list, 1); // Add node with value 1 to the linked list list = push(list, 2); // Add node with value 2 to the linked list list = push(list, 3); // Add node with value 3 to the linked list printList(list); // Print the linked list // Delete node at position 1 from the linked list list = deleteN(list, 1); printList(list); // Print the updated linked list } } |
| — |
Python3
| # Python program to implement the above approach class Node: # constructor to initialize the node object def __init__(self, data): self.number = data self.next = None def push(head, A): n = Node(A) n.number = A n.next = head head = n return head def deleteN(head, position): temp = head prev = head for i in range(0, position): if i == 0 and position == 1: head = head.next else: if i == position-1 and temp is not None: prev.next = temp.next else: prev = temp # Position was greater than # number of nodes in the list if prev is None: break temp = temp.next return head def printList(head): while(head): if head.next == None: print("[", head.number, "] ", "[", hex(id(head)), "]->", "nil") else: print("[", head.number, "] ", "[", hex( id(head)), "]->", hex(id(head.next))) head = head.next print("") print("") head = Node(0) head = push(head, 1) head = push(head, 2) head = push(head, 3) printList(head) # Delete any position from list head = deleteN(head, 1) printList(head) # This code is contributed by Yash Agawral(yashagawral2852002) |
| — |
Javascript
| class Node { constructor(number) { this.number = number; this.next = null; } } function push(head, number) { const node = new Node(number); node.next = head; head = node; return head; } function deleteN(head, position) { let temp = head; let prev = head; for (let i = 0; i < position; i++) { if (i === 0 && position === 1) { head = head.next; temp = null; } else { if (i === position - 1 && temp) { prev.next = temp.next; temp = null; } else { prev = temp; // Position was greater than // number of nodes in the list if (prev === null) break; temp = temp.next; } } } return head; } function printList(head) { while (head) { if (head.next === null) console.log([${head.number}] [${head}]->(nil)); else console.log([${head.number}] [${head}]->${head.next}); head = head.next; } console.log('\n'); } // Driver code let list = new Node(0); list.next = null; list = push(list, 1); list = push(list, 2); list = push(list, 3); printList(list); // Delete any position from list list = deleteN(list, 1); printList(list); |
| — |
C#
| using System; public class Node { public int number; public Node next; } public class Program { public static void Push(ref Node head, int A) { Node n = new Node(); n.number = A; n.next = head; head = n; } public static void deleteN(ref Node head, int position) { Node temp = head; Node prev = head; for (int i = 0; i < position; i++) { if (i == 0 && position == 1) { head = head.next; temp = null; } else { if (i == position - 1 && temp != null) { prev.next = temp.next; temp = null; } else { prev = temp; // Position was greater than // number of nodes in the list if (prev == null) { break; } temp = temp.next; } } } } public static void printList(Node head) { while (head != null) { if (head.next == null) { Console.WriteLine("[" + head.number + "] " + "[" + head + "]->" + "(nil)"); } else { Console.WriteLine("[" + head.number + "] " + "[" + head + "]->" + head.next); } head = head.next; } Console.WriteLine("\n"); } // Driver code public static void Main() { Node list = new Node(); list.next = null; Push(ref list, 1); Push(ref list, 2); Push(ref list, 3); printList(list); // Delete any position from list deleteN(ref list, 1); printList(list); } } |
| — |
Output
[3] [0x1b212c0]->0x1b212a0
[2] [0x1b212a0]->0x1b21280
[1] [0x1b21280]->0x1b21260
[0] [0x1b21260]->(nil)
[2] [0x1b212a0]->0x1b21280
[1] [0x1b21280]->0x1b21260
[0] [0x1b21260]->(nil)
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Recursive Method to delete a node from linked list:
To delete a node of a linked list recursively we need to do the following steps:
- We pass node* (node pointer) as a reference to the function (as in node* &head)
- Now since the current node pointer is derived from the previous node’s next (which is passed by reference) so now if the value of the current node pointer is changed, the previous next node’s value also gets changed which is the required operation while deleting a node (i.e points previous node’s next to current node’s (containing key) next).
- Find the node containing the given value.
- Store this node to deallocate it later using the free() function.
- Change this node pointer so that it points to its next and by performing this previous node’s next also gets properly linked.
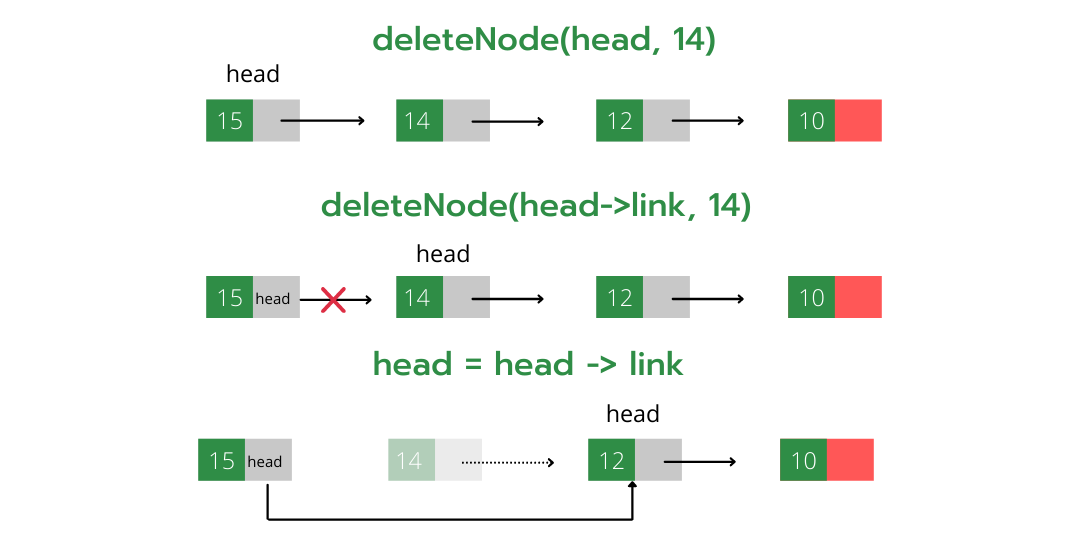
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
C++
| // C++ program to delete a node in // singly linked list recursively #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct node { int info; node* link = NULL; node() {} node(int a) : info(a) { } }; // Deletes the node containing 'info' // part as val and alter the head of // the linked list (recursive method) void deleteNode(node*& head, int val) { // Check if list is empty or we // reach at the end of the // list. if (head == NULL) { cout << "Element not present in the list\n"; return; } // If current node is the // node to be deleted if (head->info == val) { node* t = head; // If it's start of the node head // node points to second node head = head->link; // Else changes previous node's // link to current node's link delete (t); return; } deleteNode(head->link, val); } // Utility function to add a // node in the linked list // Here we are passing head by // reference thus no need to // return it to the main function void push(node*& head, int data) { node* newNode = new node(data); newNode->link = head; head = newNode; } // Utility function to print // the linked list (recursive // method) void print(node* head) { // cout<<endl gets implicitly // typecasted to bool value // 'true' if (head == NULL and cout << endl) return; cout << head->info << ' '; print(head->link); } int main() { // Starting with an empty linked list node* head = NULL; // Adds new element at the // beginning of the list push(head, 10); push(head, 12); push(head, 14); push(head, 15); // original list print(head); // Call to delete function deleteNode(head, 20); // 20 is not present thus no change // in the list print(head); deleteNode(head, 10); print(head); deleteNode(head, 14); print(head); return 0; } |
| — |
Python3
| # Python program to delete a node in # singly linked list recursively class Node: def __init__(self,data): self.data = data self.next = None # Deletes the node containing 'data' # part as val and alter the head of # the linked list (recursive method) def deleteNode(head, val): # Check if list is empty or we # reach at the end of the # list. if (head == None): print("Element not present in the list") return -1 # If current node is the # node to be deleted if (head.data == val): # If it's start of the node head # node points to second node if head.next: head.data = head.next.data head.next = head.next.next return 1 else: return 0 if deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0: head.next = None return 1 # Utility function to add a # node in the linked list # Here we are passing head by # reference thus no need to # return it to the main function def push(head, data): newNode = Node(data) newNode.next = head head = newNode return head # Utility function to print # the linked list (recursive # method) def printLL(head): if (head == None): return temp = head while temp: print(temp.data,end=' ') temp = temp.next print() # Driver Code # Starting with an empty linked list head = None # Adds new element at the # beginning of the list head = push(head, 10) head = push(head, 12) head = push(head, 14) head = push(head, 15) # original list printLL(head) # Call to delete function deleteNode(head, 20) # 20 is not present thus no change # in the list printLL(head) deleteNode(head, 10) printLL(head) deleteNode(head, 14) printLL(head) |
| — |
C#
| using System; class LinkedList { public class Node { public int info; public Node link; public Node(int a) { info = a; link = null; } } // Deletes the node containing 'info' part as val and alters the head of the linked list (recursive method) public static void deleteNode(ref Node head, int val) { // Check if list is empty or we reach at the end of the list. if (head == null) { Console.WriteLine("Element not present in the list"); return; } // If current node is the node to be deleted if (head.info == val) { Node t = head; // If it's start of the node head node points to second node head = head.link; // Delete the node t = null; return; } // Recursively call the function on the next node deleteNode(ref head.link, val); } // Utility function to add a node in the linked list. Here we are passing head by reference thus no need to return it to the main function. public static void push(ref Node head, int data) { Node newNode = new Node(data); newNode.link = head; head = newNode; } // Utility function to print the linked list (recursive method) public static void print(Node head) { // If head is null, it means we have reached the end of the list if (head == null) { Console.WriteLine(); return; } Console.Write(head.info + " "); // Recursively print the remaining nodes print(head.link); } public static void Main(string[] args) { // Starting with an empty linked list Node head = null; // Adds new element at the beginning of the list push(ref head, 10); push(ref head, 12); push(ref head, 14); push(ref head, 15); // Print the original list print(head); // Call to delete function deleteNode(ref head, 20); // 20 is not present thus no change in the list print(head); // Delete nodes and print the list after each deletion deleteNode(ref head, 10); print(head); deleteNode(ref head, 14); print(head); } } |
| — |
Javascript
| // JavaScript program to delete a node in // singly linked list recursively class Node { constructor(data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } // Deletes the node containing 'data' // part as val and alter the head of // the linked list (recursive method) function deleteNode(head, val) { // Check if list is empty or we // reach at the end of the // list. if (!head) { console.log("Element not present in the list"); return -1; } // If current node is the // node to be deleted if (head.data == val) { // If it's start of the node head // node points to second node if (head.next) { head.data = head.next.data; head.next = head.next.next; return 1; } else return 0; } if (deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0) { head.next = null; return 1; } } // Utility function to add a // node in the linked list // Here we are passing head by // reference thus no need to // return it to the main function function push(head, data) { let newNode = new Node(data); newNode.next = head; head = newNode; return head; } // Utility function to print // the linked list (recursive // method) function printLL(head) { if (!head) return; let temp = head; while (temp) { console.log(temp.data, " "); temp = temp.next; } console.log(); } // Driver Code // Starting with an empty linked list let head = null; // Adds new element at the // beginning of the list head = push(head, 10); head = push(head, 12); head = push(head, 14); head = push(head, 15); // original list printLL(head); // Call to delete function deleteNode(head, 20); // 20 is not present thus no change // in the list printLL(head); deleteNode(head, 10); printLL(head); deleteNode(head, 14); printLL(head); // This code is contributed by Prajwal Kandekar |
| — |
Java
| // Java program to delete a node in // singly linked list recursively class Node { int data; Node next; public Node(int data) { this.data = data; this.next = null; } } public class Main { // Deletes the node containing 'data' // part as val and alter the head of // the linked list (recursive method) public static int deleteNode(Node head, int val) { // Check if list is empty or we // reach at the end of the // list. if (head == null) { System.out.println("Element not present in the list"); return -1; } // If current node is the // node to be deleted if (head.data == val) { // If it's start of the node head // node points to second node if (head.next != null) { head.data = head.next.data; head.next = head.next.next; return 1; } else return 0; } if (deleteNode(head.next, val) == 0) { head.next = null; return 1; } return -1; } // Utility function to add a // node in the linked list // Here we are passing head by // reference thus no need to // return it to the main function public static Node push(Node head, int data) { Node newNode = new Node(data); newNode.next = head; head = newNode; return head; } // Utility function to print // the linked list (recursive // method) public static void printLL(Node head) { if (head == null) return; Node temp = head; while (temp != null) { System.out.print(temp.data + " "); temp = temp.next; } System.out.println(); } public static void main(String[] args) { // Starting with an empty linked list Node head = null; // Adds new element at the // beginning of the list head = push(head, 10); head = push(head, 12); head = push(head, 14); head = push(head, 15); // original list printLL(head); // Call to delete function deleteNode(head, 20); // 20 is not present thus no change // in the list printLL(head); deleteNode(head, 10); printLL(head); deleteNode(head, 14); printLL(head); } } |
| — |
Output
15 14 12 10
Element not present in the list
15 14 12 10
15 14 12
15 12
Time Complexity: O(n)
Auxiliary Space: O(n) (due to recursion call stack)
Delete a Linked List node at a given position
Insertion in a Doubly Linked List =================================
Inserting a new node in a doubly linked list is very similar to inserting new node in linked list. There is a little extra work required to maintain the link of the previous node. A node can be inserted in a Doubly Linked List in four ways:
- At the front of the DLL.
- In between two nodes
- After a given node.
- Before a given node.
- At the end of the DLL.
**Insertion at the Beginning in Doubly Linked List:**
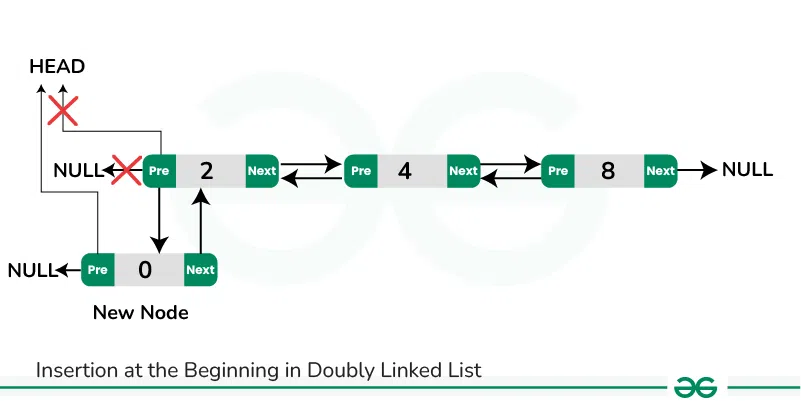
To insert a new node at the beginning of the doubly list, we can use the following steps:
- Allocate memory for a new node (say **new_node**) and assign the provided value to its data field.
- Set the previous pointer of the **new_node** to nullptr.
- If the list is empty:
- Set the next pointer of the **new_node** to nullptr.
- Update the head pointer to point to the **new_node**.
- If the list is not empty:
- Set the next pointer of the **new_node** to the current head.
- Update the previous pointer of the current head to point to the **new_node**.
- Update the head pointer to point to the **new_node**.
Below is the implementation of the 5 steps to insert a node at the front of the linked list:
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a list and an int, inserts a new node
// on the front of the list.
void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as head
// and previous as NULL
new_node->next = (*head_ref);
new_node->prev = NULL;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if ((*head_ref) != NULL)
(*head_ref)->prev = new_node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
(*head_ref) = new_node;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
// Adding a node at the front of the list
public void push(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data */
Node new_Node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as head and previous as NULL
new_Node.next = head;
new_Node.prev = null;
// 4. change prev of head node to new node
if (head != null)
head.prev = new_Node;
// 5. move the head to point to the new node
head = new_Node;
}
**Time Complexity:** O(1)
**Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
Insertion in between two nodes in Doubly Linked List:
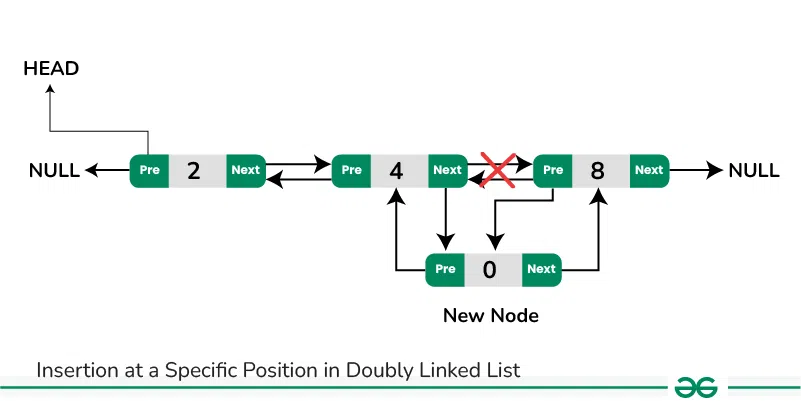
**1. Add a node after a given node in a Doubly Linked List:**
We are given a pointer to a node as **prev_node**, and the new node is inserted after the given node. This can be done using the following steps:
- Firstly create a new node (say **new_node**).
- Now insert the data in the new node.
- Point the next of **new_node** to the next of **prev_node**.
- Point the next of **prev_node** to **new_node**.
- Point the previous of **new_node** to **prev_node**.
- Point the previous of next of **new_node** to **new_node**.
Below is the implementation of the steps to insert a node after a given node in the linked list:
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertAfter(Node* prev_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_node == NULL) {
cout << "the given previous node cannot be NULL";
return;
}
// 1. allocate new node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node->next = prev_node->next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_node->next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node->prev = prev_node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node->next != NULL)
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertAfter(Node prev_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given prev_node is NULL
if (prev_Node == null) {
System.out.println(
"The given previous node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make next of new node as next of prev_node
new_node.next = prev_Node.next;
// 4. Make the next of prev_node as new_node
prev_Node.next = new_node;
// 5. Make prev_node as previous of new_node
new_node.prev = prev_Node;
// 6. Change previous of new_node's next node
if (new_node.next != null)
new_node.next.prev = new_node;
}
**Time Complexity:** O(1)
**Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
**2. Add a node before a given node in a Doubly Linked List:**
Let the pointer to this given node be **next_node**. This can be done using the following steps.
- Allocate memory for the new node, let it be called **new_node**.
- Put the data in **new_node**.
- Set the previous pointer of this **new_node** as the previous node of the **next_node**.
- Set the previous pointer of the **next_node** as the **new_node**.
- Set the next pointer of this **new_node** as the **next_node**.
- Set the next pointer of the previous of **new_node** to **new_node**.
Below is the implementation of the above approach.
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
void insertBefore(Node* next_node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_node == NULL) {
printf("the given next node cannot be NULL");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate new node
Node* new_node = new Node();
// 2. Put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of next_node
new_node->prev = next_node->prev;
// 4. Make the previous of next_node as new_node
next_node->prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node->next = next_node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node->prev != NULL)
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
// Given a node as prev_node, insert a new node
// after the given node
public void InsertBefore(Node next_Node, int new_data)
{
// Check if the given next_node is NULL
if (next_Node == null) {
System.out.println(
"The given next node cannot be NULL ");
return;
}
// 1. Allocate node
// 2. Put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
// 3. Make previous of new node as previous of prev_node
new_node.prev = next_Node.prev;
// 4. Make the prev of next_node as new_node
next_Node.prev = new_node;
// 5. Make next_node as next of new_node
new_node.next = next_Node;
// 6. Change next of new_node's previous node
if (new_node.prev != null)
new_node.prev.next = new_node;
else
head = new_node;
}
**Time Complexity:** O(1)
**Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
**Insertion at the End in Doubly Linked List:**
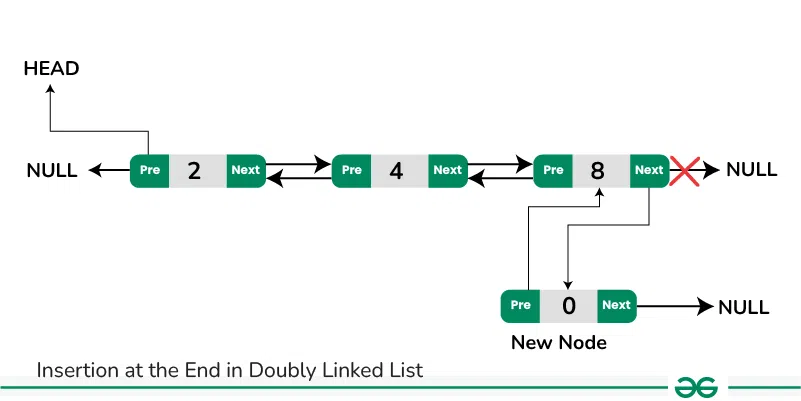
The new node is always added after the last node of the given Linked List. This can be done using the following steps:
- Create a new node (say **new_node**).
- Put the value in the new node.
- Make the next pointer of **new_node** as null.
- If the list is empty, make **new_node** as the head.
- Otherwise, travel to the end of the linked list.
- Now make the next pointer of last node point to **new_node**.
- Change the previous pointer of **new_node** to the last node of the list.
Below is the implementation of the steps to insert a node at the end of the linked list:
// Given a reference (pointer to pointer) to the head
// of a DLL and an int, appends a new node at the end
void append(Node** head_ref, int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
Node* new_node = new Node();
Node* last = *head_ref; /* used in step 5*/
// 2. put in the data
new_node->data = new_data;
// 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node->next = NULL;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
// node as head
if (*head_ref == NULL) {
new_node->prev = NULL;
*head_ref = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last->next != NULL)
last = last->next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last->next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node->prev = last;
return;
}
// This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110
// Add a node at the end of the list
void append(int new_data)
{
// 1. allocate node
// 2. put in the data
Node new_node = new Node(new_data);
Node last = head; /* used in step 5*/
// 3. This new node is going to be the last node, so
// make next of it as NULL
new_node.next = null;
// 4. If the Linked List is empty, then make the new
// node as head
if (head == null) {
new_node.prev = null;
head = new_node;
return;
}
// 5. Else traverse till the last node
while (last.next != null)
last = last.next;
// 6. Change the next of last node
last.next = new_node;
// 7. Make last node as previous of new node
new_node.prev = last;
}
**Time Complexity:** O(n)
**Auxiliary Space:** O(1)
**Related Articles:**
- Doubly Linked List meaning in DSA
- Introduction to Doubly linked List – Data Structure and Algorithm Tutorials
- Delete a node in double Link List
Operations of Doubly Linked List with Implementation
Search an element in a Doubly Linked List
Delete a node in a Doubly Linked List =====================================
Write a function to delete a given node in a doubly-linked list.
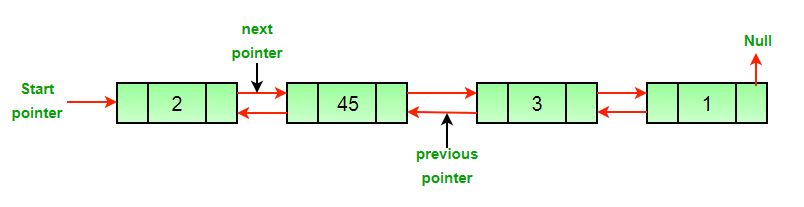
Example:
Input: DLL = 2->45->3->1, Node = 45
Output: 2->3->1Input: DLL = 2->45->3->1, Node = 1
Output: 2->45->3
Recommended Practice Delete node in Doubly Linked List
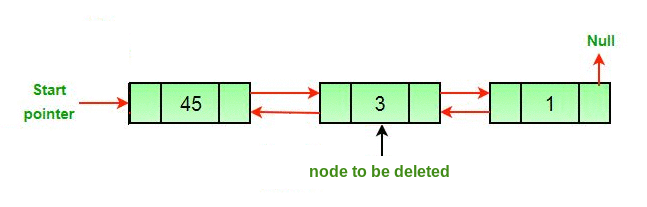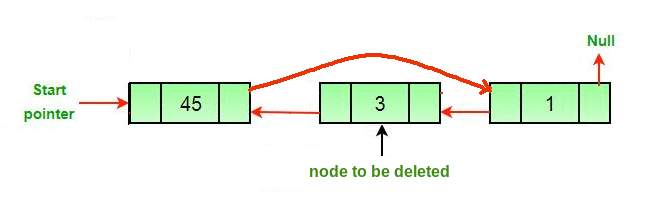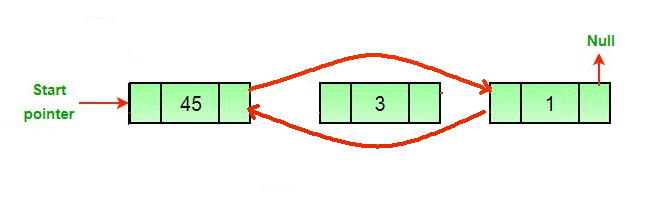
Approach: The deletion of a node in a doubly-linked list can be divided into three main categories:
- After the deletion of the head node.
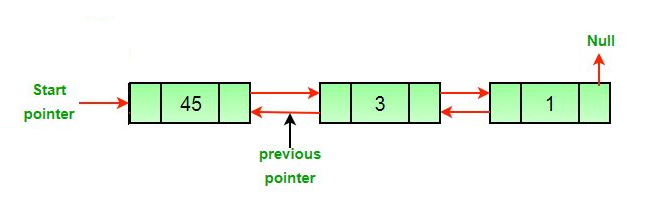
- After the deletion of the middle node.
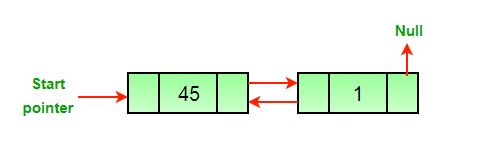
- After the deletion of the last node.
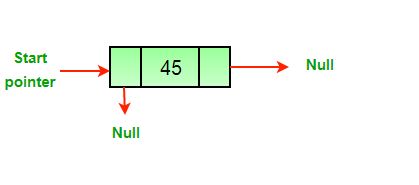
All three mentioned cases can be handled in two steps if the pointer of the node to be deleted and the head pointer is known.
- If the node to be deleted is the head node then make the next node as head.
- If a node is deleted, connect the next and previous node of the deleted node.
Algorithm:
- Let the node to be deleted be del.
- If node to be deleted is head node, then change the head pointer to next current head.
if *headnode* == *del* then
*headnode* = *del*.nextNode
- Set prev of next to del, if next to del exists.
if *del*.nextNode != *none*
*del*.nextNode.previousNode = *del*.previousNode
- Set next of previous to del, if previous to del exists.
if *del*.previousNode != *none*
*del*.previousNode.nextNode = *del*.next
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
| // C++ program to delete a node from // Doubly Linked List #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; /* a node of the doubly linked list */ class Node { public: int data; Node* next; Node* prev; }; /* Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */ void deleteNode(Node** head_ref, Node* del) { /* base case */ if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL) return; /* If node to be deleted is head node */ if (*head_ref == del) *head_ref = del->next; /* Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT the last node */ if (del->next != NULL) del->next->prev = del->prev; /* Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT the first node */ if (del->prev != NULL) del->prev->next = del->next; /* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/ free(del); return; } /* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */ /* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */ void push(Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* allocate node */ Node* new_node = new Node(); /* put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* since we are adding at the beginning, prev is always NULL */ new_node->prev = NULL; /* link the old list of the new node */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* change prev of head node to new node */ if ((*head_ref) != NULL) (*head_ref)->prev = new_node; /* move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */ void printList(Node* node) { while (node != NULL) { cout << node->data << " "; node = node->next; } } /* Driver code*/ int main() { /* Start with the empty list */ Node* head = NULL; /* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */ push(&head, 2); push(&head, 4); push(&head, 8); push(&head, 10); cout << "Original Linked list "; printList(head); /* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */ deleteNode(&head, head); /*delete first node*/ deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete middle node*/ deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete last node*/ /* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */ cout << "\nModified Linked list "; printList(head); return 0; } // This code is contributed by rathbhupendra |
| — |
C
| #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> /* a node of the doubly linked list */ struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; struct Node* prev; }; /* Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. del --> pointer to node to be deleted. */ void deleteNode(struct Node** head_ref, struct Node* del) { /* base case */ if (*head_ref == NULL || del == NULL) return; /* If node to be deleted is head node */ if (*head_ref == del) *head_ref = del->next; /* Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT the last node */ if (del->next != NULL) del->next->prev = del->prev; /* Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT the first node */ if (del->prev != NULL) del->prev->next = del->next; /* Finally, free the memory occupied by del*/ free(del); return; } /* UTILITY FUNCTIONS */ /* Function to insert a node at the beginning of the Doubly Linked List */ void push(struct Node** head_ref, int new_data) { /* allocate node */ struct Node* new_node = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); /* put in the data */ new_node->data = new_data; /* since we are adding at the beginning, prev is always NULL */ new_node->prev = NULL; /* link the old list of the new node */ new_node->next = (*head_ref); /* change prev of head node to new node */ if ((*head_ref) != NULL) (*head_ref)->prev = new_node; /* move the head to point to the new node */ (*head_ref) = new_node; } /* Function to print nodes in a given doubly linked list This function is same as printList() of singly linked list */ void printList(struct Node* node) { while (node != NULL) { printf("%d ", node->data); node = node->next; } } /* Driver program to test above functions*/ int main() { /* Start with the empty list */ struct Node* head = NULL; /* Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 */ push(&head, 2); push(&head, 4); push(&head, 8); push(&head, 10); printf("\n Original Linked list "); printList(head); /* delete nodes from the doubly linked list */ deleteNode(&head, head); /*delete first node*/ deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete middle node*/ deleteNode(&head, head->next); /*delete last node*/ /* Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL */ printf("\n Modified Linked list "); printList(head); getchar(); } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program to delete a node from // Doubly Linked List // Class for Doubly Linked List public class DLL { Node head; // head of list /* Doubly Linked list Node*/ class Node { int data; Node prev; Node next; // Constructor to create a new node // next and prev is by default initialized // as null Node(int d) { data = d; } } // Adding a node at the front of the list public void push(int new_data) { // 1. allocate node // 2. put in the data Node new_Node = new Node(new_data); // 3. Make next of new node as head // and previous as NULL new_Node.next = head; new_Node.prev = null; // 4. change prev of head node to new node if (head != null) head.prev = new_Node; // 5. move the head to point to the new node head = new_Node; } // This function prints contents of linked list // starting from the given node public void printlist(Node node) { Node last = null; while (node != null) { System.out.print(node.data + " "); last = node; node = node.next; } System.out.println(); } // Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. // head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. // del --> data of node to be deleted. void deleteNode(Node del) { // Base case if (head == null || del == null) { return; } // If node to be deleted is head node if (head == del) { head = del.next; } // Change next only if node to be deleted // is NOT the last node if (del.next != null) { del.next.prev = del.prev; } // Change prev only if node to be deleted // is NOT the first node if (del.prev != null) { del.prev.next = del.next; } // Finally, free the memory occupied by del return; } // Driver Code public static void main(String[] args) { // Start with the empty list DLL dll = new DLL(); // Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL dll.push(2); // Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL dll.push(4); // Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL dll.push(8); // Insert 10. So linked list becomes // 10->8->4->2->NULL dll.push(10); System.out.print("Original Linked list "); dll.printlist(dll.head); dll.deleteNode(dll.head); /*delete first node*/ dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); /*delete middle node*/ dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); /*delete last node*/ System.out.print( "\nModified Linked list "); dll.printlist(dll.head); } } |
| — |
Python3
| # Program to delete a node in a doubly-linked list # for Garbage collection import gc # A node of the doubly linked list class Node: # Constructor to create a new node def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = None self.prev = None class DoublyLinkedList: # Constructor for empty Doubly Linked List def __init__(self): self.head = None # Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. # head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. # dele --> pointer to node to be deleted def deleteNode(self, dele): # Base Case if self.head is None or dele is None: return # If node to be deleted is head node if self.head == dele: self.head = dele.next # Change next only if node to be deleted is NOT # the last node if dele.next is not None: dele.next.prev = dele.prev # Change prev only if node to be deleted is NOT # the first node if dele.prev is not None: dele.prev.next = dele.next # Finally, free the memory occupied by dele # Call python garbage collector gc.collect() # Given a reference to the head of a list and an # integer, inserts a new node on the front of list def push(self, new_data): # 1. Allocates node # 2. Put the data in it new_node = Node(new_data) # 3. Make next of new node as head and # previous as None (already None) new_node.next = self.head # 4. change prev of head node to new_node if self.head is not None: self.head.prev = new_node # 5. move the head to point to the new node self.head = new_node def printList(self, node): while(node is not None): print(node.data,end=' ') node = node.next # Driver program to test the above functions # Start with empty list dll = DoublyLinkedList() # Let us create the doubly linked list 10<->8<->4<->2 dll.push(2); dll.push(4); dll.push(8); dll.push(10); print ("\n Original Linked List",end=' ') dll.printList(dll.head) # delete nodes from doubly linked list dll.deleteNode(dll.head) dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next) dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next) # Modified linked list will be NULL<-8->NULL print("\n Modified Linked List",end=' ') dll.printList(dll.head) # This code is contributed by Nikhil Kumar Singh(nickzuck_007) |
| — |
C#
| // C# program to delete a node from // Doubly Linked List using System; // Class for Doubly Linked List public class DLL { Node head; // head of list /* Doubly Linked list Node*/ public class Node { public int data; public Node prev; public Node next; // Constructor to create a new node // next and prev is by default // initialized as null public Node(int d) { data = d; } } // Adding a node at the front of the list public void push(int new_data) { // 1. allocate node // 2. put in the data Node new_Node = new Node(new_data); // 3. Make next of new node as head // and previous as NULL new_Node.next = head; new_Node.prev = null; // 4. change prev of head node to new node if (head != null) head.prev = new_Node; // 5. move the head to point to the new node head = new_Node; } // This function prints contents of linked list // starting from the given node public void printlist(Node node) { while (node != null) { Console.Write(node.data + " "); node = node.next; } Console.WriteLine(); } // Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. // head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. // del --> data of node to be deleted. void deleteNode(Node del) { // Base case if (head == null || del == null) { return; } // If node to be deleted is head node if (head == del) { head = del.next; } // Change next only if node to be deleted // is NOT the last node if (del.next != null) { del.next.prev = del.prev; } // Change prev only if node to be deleted // is NOT the first node if (del.prev != null) { del.prev.next = del.next; } // Finally, free the memory occupied by del return; } // Driver Code public static void Main() { // Start with the empty list DLL dll = new DLL(); // Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL dll.push(2); // Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL dll.push(4); // Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL dll.push(8); // Insert 10. So linked list becomes 10->8->4->2->NULL dll.push(10); Console.Write("Original Linked list "); dll.printlist(dll.head); // Deleting first node dll.deleteNode(dll.head); dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); dll.deleteNode(dll.head.next); Console.Write("Modified Linked list "); dll.printlist(dll.head); } } // This code is contributed by PrinciRaj1992 |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> // Javascript program to delete a node from // Doubly Linked List // Class for Doubly Linked List var head; // head of list /* Doubly Linked list Node */ class Node { // Constructor to create a new node // next and prev is by default initialized // as null constructor(val) { this.data = val; this.prev = null; this.next = null; } } // Adding a node at the front of the list function push(new_data) { // 1. allocate node // 2. put in the data new_Node = new Node(new_data); // 3. Make next of new node as head // and previous as NULL new_Node.next = head; new_Node.prev = null; // 4. change prev of head node to new node if (head != null) head.prev = new_Node; // 5. move the head to point to the new node head = new_Node; } // This function prints contents of linked list // starting from the given node function printlist( node) { last = null; while (node != null) { document.write(node.data + " "); last = node; node = node.next; } document.write("<br/>"); } // Function to delete a node in a Doubly Linked List. // head_ref --> pointer to head node pointer. // del --> data of node to be deleted. function deleteNode( del) { // Base case if (head == null || del == null) { return; } // If node to be deleted is head node if (head == del) { head = del.next; } // Change next only if node to be deleted // is NOT the last node if (del.next != null) { del.next.prev = del.prev; } // Change prev only if node to be deleted // is NOT the first node if (del.prev != null) { del.prev.next = del.next; } // Finally, free the memory occupied by del return; } // Driver Code // Start with the empty list // Insert 2. So linked list becomes 2->NULL push(2); // Insert 4. So linked list becomes 4->2->NULL push(4); // Insert 8. So linked list becomes 8->4->2->NULL push(8); // Insert 10. So linked list becomes 10->8->4->2->NULL push(10); document.write("Created DLL is: "); printlist(head); // Deleting first node deleteNode(head); deleteNode(head.next); deleteNode(head.next); document.write("Modified Linked list: "); printlist(head); // This code is contributed by todaysgaurav </script> |
| — |
Output
Original Linked list 10 8 4 2
Modified Linked list 8
Complexity Analysis:
- Time Complexity: O(1).
Since traversal of the linked list is not required so the time complexity is constant. - Auxiliary Space: O(1).
As no extra space is required, so the space complexity is constant.
Search an element in a Doubly Linked List
Delete a Doubly Linked List node at a given position
Circular Singly Linked List | Insertion =======================================
We have discussed Singly and Circular Linked List in the following post:
Singly Linked List
Circular Linked List
Why Circular linked list?
In a singly linked list, for accessing any node of the linked list, we start traversing from the first node. If we are at any node in the middle of the list, then it is not possible to access nodes that precede the given node. This problem can be solved by slightly altering the structure of a singly linked list. In a singly linked list, the next part (pointer to the next node) of the last node is NULL. If we utilize this link to point to the first node, then we can reach the preceding nodes. Refer to this for more advantages of circular linked lists.
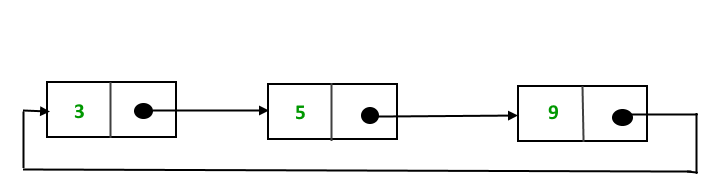
In this post, the implementation and insertion of a node in a Circular Linked List using a singly linked list are explained.
Implementation of circular linked list:
To implement a circular singly linked list, we take an external pointer that points to the last node of the list. If we have a pointer last pointing to the last node, then last -> next will point to the first node.
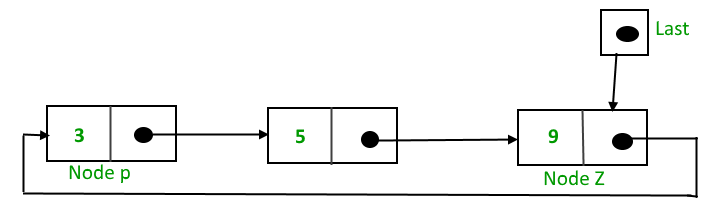
The pointer last points to node Z and last -> next points to node P.
Why have we taken a pointer that points to the last node instead of the first node?
For the insertion of a node at the beginning, we need to traverse the whole list. Also, for insertion at the end, the whole list has to be traversed. If instead of the start pointer, we take a pointer to the last node, then in both cases there won’t be any need to traverse the whole list. So insertion at the beginning or at the end takes constant time, irrespective of the length of the list.
Insertion in a circular linked list:
A node can be added in three ways:
- Insertion in an empty list
- Insertion at the beginning of the list
- Insertion at the end of the list
- Insertion in between the nodes
Insertion in an empty List:
Initially, when the list is empty, the last pointer will be NULL.

After inserting node T,
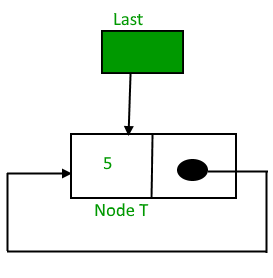
After insertion, T is the last node, so the pointer last points to node T. And Node T is the first and the last node, so T points to itself.
Below is the implementation of the above operation:
C++
| // C++ program for the above operation struct Node* addToEmpty(struct Node* last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != NULL) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Assigning the data. temp->data = data; last = temp; // Note : list was empty. We link single node // to itself. temp->next = last; return last; } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program for the above operation static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Note : list was empty. We link single node // to itself. temp.next = last; return last; } // This code is contributed by gauravrajput1 |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program for the above operation def addToEmpty(self, data): if (self.last != None): return self.last # Creating the newnode temp temp = Node(data) self.last = temp # Creating the link self.last.next = self.last return self.last # this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| // C# program for the above operation static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Note : list was empty. We link single node // to itself. temp.next = last; return last; } // This code contributed by umadevi9616 |
| — |
Javascript
| // Javascript program for the above operation function addToEmpty(last , data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. var temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Note : list was empty. We link single node // to itself. temp.next = last; return last; } // This code contributed by umadevi9616 |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(1), As we have to perform constant number of operations.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), As constant extra space is used.
Insertion at the beginning of the list
To insert a node at the beginning of the list, follow these steps:
- Create a node, say T
- Make T -> next = last -> next
- last -> next = T
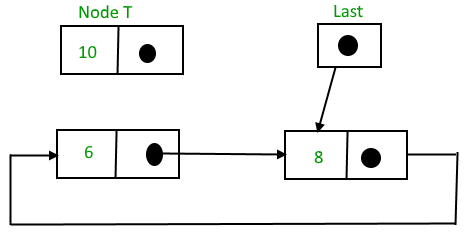
After insertion,
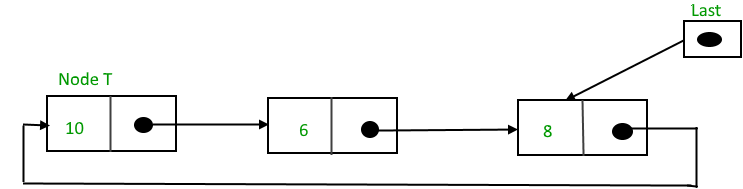
Below is the implementation of the above operation:
C++
| // C++ program for the above operation struct Node* addBegin(struct Node* last, int data) { if (last == NULL) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically. struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Assigning the data. temp->data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp->next = last->next; last->next = temp; return last; } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program for the above operation static Node addBegin(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data temp.data = data; // Adjusting the links temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } // This code is contributed by rutvik_56 |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program for the above operation def addBegin(self, data): if (self.last == None): return self.addToEmpty(data) temp = Node(data) temp.next = self.last.next self.last.next = temp return self.last # this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| // C# program for the above operation static Node addBegin(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data temp.data = data; // Adjusting the links temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } // This code is contributed by Pratham76 |
| — |
Javascript
| // Javascript program for the above operation function addBegin(last , data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically. var temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } // This code contributed by Shivani |
| — |
Time complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Insertion at the end of the list
To insert a node at the end of the list, follow these steps:
- Create a node, say T
- Make T -> next = last -> next
- last -> next = T
- last = T
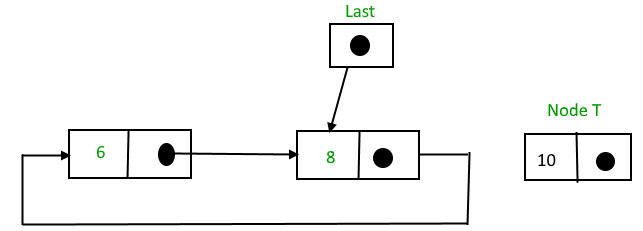
After insertion
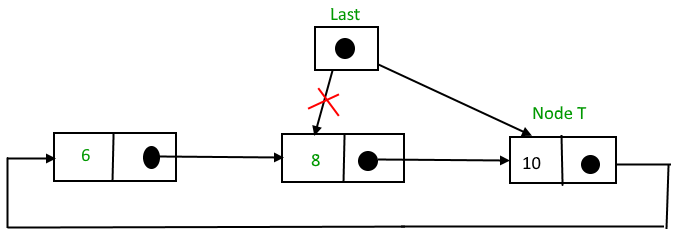
Below is the implementation of the above operation:
C++
| // C++ program for the above operation struct Node* addEnd(struct Node* last, int data) { if (last == NULL) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically. struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Assigning the data. temp->data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp->next = last->next; last->next = temp; last = temp; return last; } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program for the above operation static Node addEnd(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically. Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program for the above operation def addEnd(self, data): if (self.last == None): return self.addToEmpty(data) # Assigning the data. temp = Node(data) # Adjusting the links. temp.next = self.last.next self.last.next = temp self.last = temp return self.last # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| // C# program for the above operation static Node addEnd(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); // Creating a node dynamically. Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Javascript
| // Javascript program for the above operation function addEnd(last, data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); var temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } // this code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(1)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Insertion in between the nodes
To insert a node in between the two nodes, follow these steps:
- Create a node, say T.
- Search for the node after which T needs to be inserted, say that node is P.
- Make T -> next = P -> next;
- P -> next = T.
Suppose 12 needs to be inserted after the node that has the value 8,
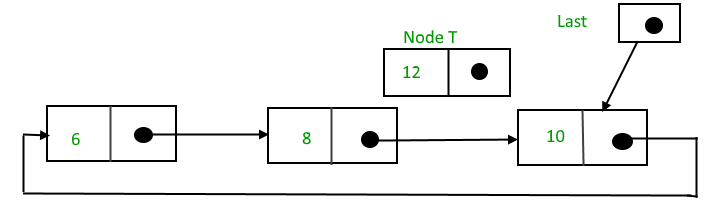
After searching and insertion,
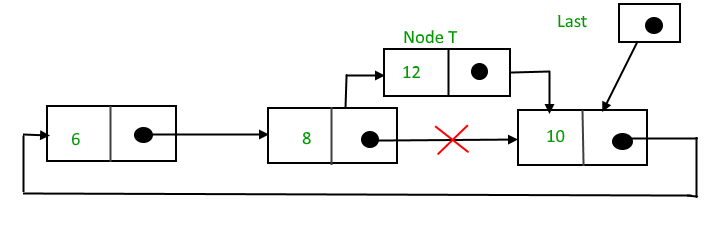
Below is the implementation of the above operation:
C++
| // C++ program for the above operation struct Node* addAfter(struct Node* last, int data, int item) { if (last == NULL) return NULL; struct Node *temp, *p; p = last->next; // Searching the item. do { if (p->data == item) { // Creating a node dynamically. temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Assigning the data. temp->data = data; // Adjusting the links. temp->next = p->next; // Adding newly allocated node after p. p->next = temp; // Checking for the last node. if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p->next; } while (p != last->next); cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl; return last; } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program for the above operation static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item) { if (last == null) return null; Node temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); System.out.println(item + " not present in the list."); return last; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program for the above operation def addAfter(self, data, item): if (self.last == None): return None temp = Node(data) p = self.last.next while p: if (p.data == item): temp.next = p.next p.next = temp if (p == self.last): self.last = temp return self.last else: return self.last p = p.next if (p == self.last.next): print(item, "not present in the list") break # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| // C# program for the above operation static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item) { if (last == null) return null; Node temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list."); return last; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Javascript
| // Javascript program for the above operation function addAfter(last, data, item) { if (last == null) return null; var temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); document.write(item + " not present in the list. <br>"); return last; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Below is a complete program that uses all of the above methods to create a circular singly linked list.
C++
| // C++ program for the above methods #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; struct Node { int data; struct Node* next; }; struct Node* addToEmpty(struct Node* last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != NULL) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); // Assigning the data. temp->data = data; last = temp; // Creating the link. last->next = last; return last; } struct Node* addBegin(struct Node* last, int data) { if (last == NULL) return addToEmpty(last, data); struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->data = data; temp->next = last->next; last->next = temp; return last; } struct Node* addEnd(struct Node* last, int data) { if (last == NULL) return addToEmpty(last, data); struct Node* temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->data = data; temp->next = last->next; last->next = temp; last = temp; return last; } struct Node* addAfter(struct Node* last, int data, int item) { if (last == NULL) return NULL; struct Node *temp, *p; p = last->next; do { if (p->data == item) { temp = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); temp->data = data; temp->next = p->next; p->next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p->next; } while (p != last->next); cout << item << " not present in the list." << endl; return last; } void traverse(struct Node* last) { struct Node* p; // If list is empty, return. if (last == NULL) { cout << "List is empty." << endl; return; } // Pointing to first Node of the list. p = last->next; // Traversing the list. do { cout << p->data << " "; p = p->next; } while (p != last->next); } // Driver code int main() { struct Node* last = NULL; last = addToEmpty(last, 6); last = addBegin(last, 4); last = addBegin(last, 2); last = addEnd(last, 8); last = addEnd(last, 12); last = addAfter(last, 10, 8); // Function call traverse(last); return 0; } |
| — |
Java
| // Java program for the above methods public class GFG { static class Node { int data; Node next; }; static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Creating the link. last.next = last; return last; } static Node addBegin(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); Node temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } static Node addEnd(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); Node temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item) { if (last == null) return null; Node temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); System.out.println(item + " not present in the list."); return last; } static void traverse(Node last) { Node p; // If list is empty, return. if (last == null) { System.out.println("List is empty."); return; } // Pointing to first Node of the list. p = last.next; // Traversing the list. do { System.out.print(p.data + " "); p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); } // Driver code public static void main(String[] args) { Node last = null; last = addToEmpty(last, 6); last = addBegin(last, 4); last = addBegin(last, 2); last = addEnd(last, 8); last = addEnd(last, 12); last = addAfter(last, 10, 8); // Function call traverse(last); } } /* This code contributed by PrinciRaj1992 */ // This code is updated by Susobhan AKhuli |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program for the above methods class Node: def __init__(self, data): self.data = data self.next = 0 class CircularLinkedList: def __init__(self): self.last = None # This function is only for empty list def addToEmpty(self, data): if (self.last != None): return self.last # Creating the newnode temp temp = Node(data) self.last = temp # Creating the link self.last.next = self.last return self.last def addBegin(self, data): if (self.last == None): return self.addToEmpty(data) temp = Node(data) temp.next = self.last.next self.last.next = temp return self.last def addEnd(self, data): if (self.last == None): return self.addToEmpty(data) temp = Node(data) temp.next = self.last.next self.last.next = temp self.last = temp return self.last def addAfter(self, data, item): if (self.last == None): return None temp = Node(data) p = self.last.next while p: if (p.data == item): temp.next = p.next p.next = temp if (p == self.last): self.last = temp return self.last else: return self.last p = p.next if (p == self.last.next): print(item, "not present in the list") break def traverse(self): if (self.last == None): print("List is empty") return temp = self.last.next while temp: print(temp.data, end=" ") temp = temp.next if temp == self.last.next: break # Driver Code if __name__ == '__main__': llist = CircularLinkedList() last = llist.addToEmpty(6) last = llist.addBegin(4) last = llist.addBegin(2) last = llist.addEnd(8) last = llist.addEnd(12) last = llist.addAfter(10, 8) llist.traverse() # This code is contributed by # Aditya Singh |
| — |
C#
| // C# program for the above methods using System; public class GFG { public class Node { public int data; public Node next; }; static Node addToEmpty(Node last, int data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. Node temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Creating the link. last.next = last; return last; } static Node addBegin(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); Node temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } static Node addEnd(Node last, int data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); Node temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } static Node addAfter(Node last, int data, int item) { if (last == null) return null; Node temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); Console.WriteLine(item + " not present in the list."); return last; } static void traverse(Node last) { Node p; // If list is empty, return. if (last == null) { Console.WriteLine("List is empty."); return; } // Pointing to first Node of the list. p = last.next; // Traversing the list. do { Console.Write(p.data + " "); p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); } // Driver code public static void Main(String[] args) { Node last = null; last = addToEmpty(last, 6); last = addBegin(last, 4); last = addBegin(last, 2); last = addEnd(last, 8); last = addEnd(last, 12); last = addAfter(last, 10, 8); // Function call traverse(last); } } // This code contributed by Rajput-Ji |
| — |
Javascript
| class Node { constructor() { this.data = 0; this.next = null; } } function addToEmpty(last, data) { // This function is only for empty list if (last != null) return last; // Creating a node dynamically. var temp = new Node(); // Assigning the data. temp.data = data; last = temp; // Creating the link. last.next = last; return last; } function addBegin(last, data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); var temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; return last; } function addEnd(last, data) { if (last == null) return addToEmpty(last, data); var temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = last.next; last.next = temp; last = temp; return last; } function addAfter(last, data, item) { if (last == null) return null; var temp, p; p = last.next; do { if (p.data == item) { temp = new Node(); temp.data = data; temp.next = p.next; p.next = temp; if (p == last) last = temp; return last; } p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); document.write(item + " not present in the list. <br>"); return last; } function traverse(last) { var p; // If list is empty, return. if (last == null) { document.write("List is empty.<br>"); return; } // Pointing to first Node of the list. p = last.next; // Traversing the list. do { document.write(p.data + " "); p = p.next; } while (p != last.next); } // Driver code var last = null; last = addToEmpty(last, 6); last = addBegin(last, 4); last = addBegin(last, 2); last = addEnd(last, 8); last = addEnd(last, 12); last = addAfter(last, 10, 8); traverse(last); |
| — |
Output
2 4 6 8 10 12
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1), as we are not using any extra space.
Insertion Sort for Singly Linked List
Deletion at different positions in a Circular Linked List =========================================================
tGiven a Circular Linked List. The task is to write programs to delete nodes from this list present at:
- First position.
- Last Position.
- At any given position
 .
.
Deleting first node from Singly Circular Linked List
Examples:
**Input** : 99->11->22->33->44->55->66
**Output** : 11->22->33->44->55->66
**Input** : 11->22->33->44->55->66
**Output** : 22->33->44->55->66
 Deleting First Node from Circular Linked List
Deleting First Node from Circular Linked List
Approach:
- Take two pointers current and previous and traverse the list.
- Keep the pointer current fixed pointing to the first node and move previous until it reaches the last node.
-
Once, the pointer previous reaches the last node, do the following:
- previous->next = current-> next
- head = previous -> next;
Implementation: Function to delete first node from singly circular linked list.
C++
| // Function to delete First node of// Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteFirst(struct Node** head){struct Node *previous = *head, *firstNode = *head; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nList is empty\n");return;} // check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous->next == previous) {*head = NULL;return;} // traverse second node to firstwhile (previous->next != *head) { previous = previous->next;} // now previous is last node and// first node(firstNode) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious->next = firstNode->next; // make second node as head node*head = previous->next;free(firstNode);return;} |
| — |
Java
| // Function to delete First node of// Circular Linked Liststatic void DeleteFirst(Node head){Node previous = head, firstNode = head; // Check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null) {System.out.printf("\nList is empty\n");return;} // Check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous){head = null;return;} // Traverse second node to firstwhile (previous.next != head) {previous = previous.next;} // Now previous is last node and// first node(firstNode) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = firstNode.next; // Make second node as head nodehead = previous.next;System.gc();return;} // This code is contributed by aashish1995 |
| — |
Python3
| # Function delete First node of# Circular Linked Listdef DeleteFirst(head):previous = headnext = head # check list have any node# if not then returnif (head == None) : print("\nList is empty")return None # check list have single node# if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous) : head = Nonereturn None # traverse second to firstwhile (previous.next != head):previous = previous.nextnext = previous.next # now previous is last node and# next is first node of list# first node(next) link address# put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = next.next # make second node as head nodehead = previous.next return head # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| using System; public class GFG{ static public// Function delete First node of // Circular Linked List static Node DeleteFirst(Node head) { Node previous = head, next = head; // check list have any node // if not then return if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nList is empty\n"); return null; } // Check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous) { head = null; return null; } // Traverse second node to first while (previous.next != head) { previous = previous.next; next = previous.next; } // Now previous is last node and// first node(firstNode) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = next.next; // Make second node as head nodehead = previous.next; return head; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110.c void Main (){ // Code} |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> function DeleteFirst(head){previous = head, firstNode = head; // Check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){document.write("<br>List is empty<br>");return;} // Check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous){head = null;return;} // Traverse second node to firstwhile (previous.next != head){previous = previous.next;} // Now previous is last node and// first node(firstNode) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = firstNode.next; // Make second node as head nodehead = previous.next; return;} // This code is contributed by rag2127</script> |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(N), where N is the number of nodes in the Linked List.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Deleting the last node of the Circular Linked List
Examples:
**Input** : 99->11->22->33->44->55->66
**Output** : 99->11->22->33->44->55
**Input** : 99->11->22->33->44->55
**Output** : 99->11->22->33->44
 Delete last node from Circular Linked List
Delete last node from Circular Linked List
Approach:
- Take two pointers current and previous and traverse the list.
- Move both pointers such that next of previous is always pointing to current. Keep moving the pointers current and previous until current reaches the last node and previous is at the second last node.
-
Once, the pointer current reaches the last node, do the following:
- previous->next = current-> next
- head = previous -> next;
Function to delete last node from the list:
C++
| // Function delete last node of// Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteLast(struct Node** head){struct Node *current = *head, *temp = *head, *previous; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nList is empty\n");return;} // check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current->next == current) {*head = NULL;return;} // move first node to last// previouswhile (current->next != *head) {previous = current;current = current->next;} previous->next = current->next;*head = previous->next;free(current);return;} |
| — |
Java
| // Function to delete last node of// Circular Linked Liststatic Node DeleteLast(Node head){Node current = head, temp = head, previous = null; // Check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){System.out.printf("\nList is empty\n");return null;} // Check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current) {head = null;return null;} // Move first node to last// previouswhile (current.next != head){previous = current;current = current.next;} previous.next = current.next;head = previous.next; return head;} // This code is contributed by pratham76 |
| — |
Python3
| # Function to delete last node of# Circular Linked Listdef DeleteLast(head):current = headtemp = headprevious = None # check if list doesn't have any node# if not then returnif (head == None):print("\nList is empty")return None # check if list have single node# if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current):head = Nonereturn None # move first node to last# previouswhile (current.next != head):previous = currentcurrent = current.next previous.next = current.nexthead = previous.next return head # This code is contributed by rutvik_56 |
| — |
C#
| // Function to delete last node of // Circular Linked List static Node DeleteLast(Node head) { Node current = head, temp = head, previous = null; // check if list doesn't have any node // if not then return if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nList is empty\n"); return null; } // check if list have single node // if yes then delete it and return if (current.next == current) { head = null; return null; } // move first node to last // previous while (current.next != head) { previous = current; current = current.next; } previous.next = current.next; head = previous.next; return head; } // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> function DeleteLast(head){let current = head, temp = head, previous = null; // Check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){document.write("<br>List is empty<br>");return null;} // Check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current){head = null;return null;} // Move first node to last// previouswhile (current.next != head){previous = current;current = current.next;} previous.next = current.next;head = previous.next; return head;} // This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155 </script> |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes in given Linked List.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
### Deleting nodes at given index in the Circular linked list
Examples:
**Input** : 99->11->22->33->44->55->66
Index= 4
**Output** : 99->11->22->33->55->66
**Input** : 99->11->22->33->44->55->66
Index= 2
**Output** : 99->11->33->44->55->66
Note: 0-based indexing is considered for the list.
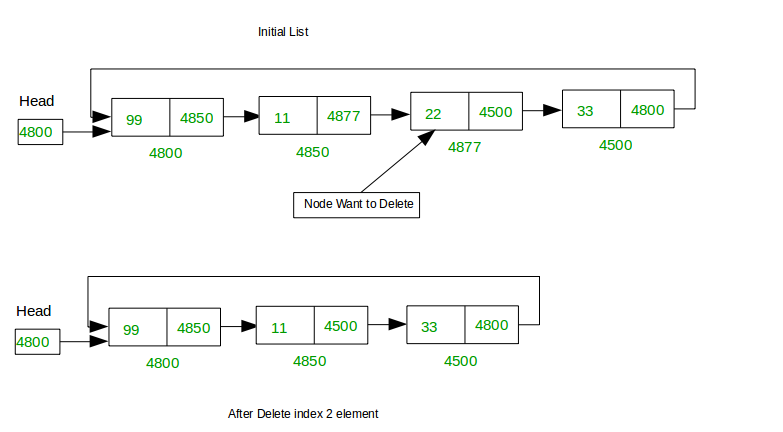
Approach:
- First, find the length of the list. That is, the number of nodes in the list.
- Take two pointers previous and current to traverse the list. Such that previous is one position behind the current node.
- Take a variable count initialized to 0 to keep track of the number of nodes traversed.
- Traverse the list until the given index is reached.
- Once the given index is reached, do previous->next = current->next.
Function to delete a node at given index or location from singly circular linked list:
C++
| // Function to delete node at given index// of Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteAtPosition(Node* head, int index){ // find length of listint len = Length(head);int count = 1;Node* previous = head;Node* next = head; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif(head == NULL){cout<<"Delete Last list is empty";return;} // given index is in list or notif(index >= len || index<0){cout<<"Index is not Found";return;} // delete first nodeif(index == 0){DeleteFirst(head);return;} // traverse first to last nodewhile(len > 0){// if index found delete that nodeif(index == count){previous->next = next->next;free(next);return;}previous = previous->next;next = previous->next;len--;count++;}return;} // This code is contributed by Yash Agarwal(yashagarwal2852002) |
| — |
C
| // Function to delete node at given index// of Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteAtPosition(struct Node** head, int index){// find length of listint len = Length(*head);int count = 1;struct Node *previous = *head, *next = *head; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nDelete Last List is empty\n");return;} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {printf("\nIndex is not Found\n");return;} // delete first nodeif (index == 0) {DeleteFirst(head);return;} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0) { // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count) {previous->next = next->next;free(next);return;}previous = previous->next;next = previous->next;len--;count++;} return;} |
| — |
Java
| // Java program to delete node at different // Function delete node at a given position// of Circular Linked Liststatic Node DeleteAtPosition( Node head, int index){// Find length of listint len = Length(head);int count = 1;Node previous = head, next = head; // check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){System.out.printf("\nDelete Last List is empty\n");return null;} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {System.out.printf("\nIndex is not Found\n");return null;} // delete first nodeif (index == 0) {head = DeleteFirst(head);return head;} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0){ // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count){previous.next = next.next; return head;}previous = previous.next;next = previous.next;len--;count++;}return head;} // This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
Python3
| # Function delete node at a given position# of Circular Linked Listdef DeleteAtPosition(head, index): # Find length of listlen = Length(head)count = 1previous = headnext = head # check list have any node# if not then returnif (head == None):print("\nDelete Last List is empty")return None # given index is in list or notif (index >= len or index < 0) :print("\nIndex is not Found")return None # delete first nodeif (index == 0) :head = DeleteFirst(head)return head # traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0): # if index found delete that nodeif (index == count):previous.next = next.next return head previous = previous.nextnext = previous.nextlen = len - 1count = count + 1 return head # This code is contributed by shivanisinghss2110 |
| — |
C#
| // C# program to delete node at given index// of circular linked list static void DeleteAtPosition(Node head, int index){// find length of listint len = Length(head);int count = 1;Node previous = head;Node next = head; // check if list doesn't have any node// if noth then returnif (head == null) {Console.Write("Delete Last list is empty");return;}// given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {Console.Write("Index is not Found");return;} // delete first nodeif (index == 0) {DeleteFirst(head);return;} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0) {// if index found delete that nodeif (index == count) {previous.next = next.next;return;}previous = previous.next;next = previous.next;len -= 1;count++;}} // this code is contributed by Kirti// Agarwal(kirtiagarwal23121999) |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> // Function delete node at a given position// of Circular Linked Listfunction DeleteAtPosition(head, index){ // Find length of listlet len = head.lengthlet count = 1let previous = headlet next = head // check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){document.write("</br>","Delete Last List is empty")return null} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0){document.write("</br>","Index is not Found")return null} // delete first nodeif (index == 0){head = DeleteFirst(head)return head} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0){ // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count){previous.next = next.next return head} previous = previous.nextnext = previous.nextlen = len - 1count = count + 1} return head } // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra </script> |
| — |
Time Complexity: O(N)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Program implementing all of the above three functions
C++
| // C++ program to delete node at different// positions from a circular linked list#include <bits/stdc++.h>using namespace std; // structure for a nodestruct Node {int data;struct Node* next;}; // Function to insert a node at the end of// a Circular linked listvoid Insert(struct Node** head, int data){struct Node* current = *head;// Create a new nodestruct Node* newNode = new Node; // check node is created or notif (!newNode) {printf("\nMemory Error\n");return;} // insert data into newly created nodenewNode->data = data; // check list is empty// if not have any node then// make first node itif (*head == NULL) {newNode->next = newNode;*head = newNode;return;} // if list have already some nodeelse { // move first node to last nodewhile (current->next != *head) {current = current->next;} // put first or head node address// in new node linknewNode->next = *head; // put new node address into last// node link(next)current->next = newNode;}} // Function print data of listvoid Display(struct Node* head){struct Node* current = head; // if list is empty, simply show messageif (head == NULL) {printf("\nDisplay List is empty\n");return;} // traverse first to last nodeelse {do {printf("%d ", current->data);current = current->next;} while (current != head);}} // Function return number of nodes present in listint Length(struct Node* head){struct Node* current = head;int count = 0; // if list is empty simply return length zeroif (head == NULL) {return 0;} // traverse first to last nodeelse {do {current = current->next;count++;} while (current != head);}return count;} // Function delete First node of Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteFirst(struct Node** head){struct Node *previous = *head, *next = *head; // check list have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nList is empty\n");return;} // check list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous->next == previous) {*head = NULL;return;} // traverse second to firstwhile (previous->next != *head) { previous = previous->next;next = previous->next;} // now previous is last node and// next is first node of list// first node(next) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious->next = next->next; // make second node as head node*head = previous->next;free(next); return;} // Function to delete last node of// Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteLast(struct Node** head){struct Node *current = *head, *temp = *head, *previous; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nList is empty\n");return;} // check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current->next == current) {*head = NULL;return;} // move first node to last// previouswhile (current->next != *head) {previous = current;current = current->next;} previous->next = current->next;*head = previous->next;free(current); return;} // Function delete node at a given position// of Circular Linked Listvoid DeleteAtPosition(struct Node** head, int index){// Find length of listint len = Length(*head);int count = 1;struct Node *previous = *head, *next = *head; // check list have any node// if not then returnif (*head == NULL) {printf("\nDelete Last List is empty\n");return;} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {printf("\nIndex is not Found\n");return;} // delete first nodeif (index == 0) {DeleteFirst(head);return;} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0) { // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count) {previous->next = next->next;free(next);return;}previous = previous->next;next = previous->next;len--;count++;}return;} // Driver Codeint main(){struct Node* head = NULL;Insert(&head, 99);Insert(&head, 11);Insert(&head, 22);Insert(&head, 33);Insert(&head, 44);Insert(&head, 55);Insert(&head, 66); // Deleting Node at positionprintf("Initial List: ");Display(head);printf("\nAfter Deleting node at index 4: ");DeleteAtPosition(&head, 4);Display(head); // Deleting first Nodeprintf("\n\nInitial List: ");Display(head);printf("\nAfter Deleting first node: ");DeleteFirst(&head);Display(head); // Deleting last Nodeprintf("\n\nInitial List: ");Display(head);printf("\nAfter Deleting last node: ");DeleteLast(&head);Display(head); return 0;} |
| — |
Java
| // Java implementation to delete node at different// positions from a circular linked listimport java.util.*; public class GFG {// structure for a nodestatic class Node {int data;Node next;}; // Function to insert a node at the end of// a Circular linked liststatic Node Insert(Node head, int data){Node current = head; // Create a new nodeNode newNode = new Node(); // check node is created or notif (newNode == null) {System.out.printf("\nMemory Error\n");return null;}// insert data into newly created nodenewNode.data = data;// check list is empty// if not have any node then// make first node itif (head == null) {newNode.next = newNode;head = newNode;return head;} else {// move first node to last nodewhile (current.next != head) {current = current.next;}// put first or head node address// in new node linknewNode.next = head;// put new node address into last// node link(next)current.next = newNode;}return head;} // function to print the data of linked liststatic void Display(Node head){Node current = head;// if list is empty, simply show messageif (head == null) {System.out.printf("\nDisplay List is empty\n");return;} else {do {System.out.printf("%d ", current.data);current = current.next;} while (current != head);}} // returns the number of nodes present in the linked liststatic int Length(Node head){Node current = head;int count = 0;// if list is empty// simply return length zeroif (head == null) return 0;else {do {current = current.next;count++;} while (current != head);}return count;} // function to delete First node of// circular Linked Liststatic Node DeleteFirst(Node head){Node previous = head, next = head;// check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null) {System.out.printf("\nList is empty\n");return null;} // check list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous) {head = null;return null;} // traverse second to firstwhile (previous.next != head) {previous = previous.next;next = previous.next;} // now previous is last node and// next is first node of list// first node(next) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = next.next; // make second node as head nodehead = previous.next; return head;} // Function to delete last node of// Circular Linked Liststatic Node DeleteLast(Node head){Node current = head, temp = head, previous = null; // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null) {System.out.printf("\nList is empty\n");return null;} // check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current) {head = null;return null;} // move first node to last// previouswhile (current.next != head) {previous = current;current = current.next;} previous.next = current.next;head = previous.next; return head;} // Function delete node at a given position// of Circular Linked Liststatic Node DeleteAtPosition(Node head, int index){// Find length of listint len = Length(head);int count = 1;Node previous = head, next = head; // check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null) {System.out.printf("\nDelete Last List is empty\n");return null;} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {System.out.printf("\nIndex is not Found\n");return null;} // delete first nodeif (index == 0) {head = DeleteFirst(head);return head;} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0) { // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count) {previous.next = next.next; return head;}previous = previous.next;next = previous.next;len--;count++;}return head;} // Driver Codepublic static void main(String args[]){Node head = null;head = Insert(head, 99);head = Insert(head, 11);head = Insert(head, 22);head = Insert(head, 33);head = Insert(head, 44);head = Insert(head, 55);head = Insert(head, 66); // Deleting Node at positionSystem.out.printf("Initial List: ");Display(head);System.out.printf("\nAfter Deleting node at index 4: ");head = DeleteAtPosition(head, 4);Display(head); // Deleting first NodeSystem.out.printf("\n\nInitial List: ");Display(head);System.out.printf("\nAfter Deleting first node: ");head = DeleteFirst(head);Display(head); // Deleting last NodeSystem.out.printf("\n\nInitial List: ");Display(head);System.out.printf("\nAfter Deleting last node: ");head = DeleteLast(head);Display(head);}}// THIS CODE IS CONTRIBUTED BY YASH AGARWAL(YASHAGARWAL2852002) |
| — |
Python3
| # Python3 program to delete node at different# positions from a circular linked list # A linked list nodeclass Node: def __init__(self, new_data): self.data = new_data self.next = Noneself.prev = None # Function to insert a node at the end of# a Circular linked listdef Insert(head, data): current = head # Create a new nodenewNode = Node(0) # check node is created or notif (newNode == None): print("\nMemory Error\n")return None # insert data into newly created nodenewNode.data = data # check list is empty# if not have any node then# make first node itif (head == None) :newNode.next = newNodehead = newNodereturn head # if list have already some nodeelse: # move first node to last nodewhile (current.next != head): current = current.next # put first or head node address# in new node linknewNode.next = head # put new node address into last# node link(next)current.next = newNode return head # Function print data of listdef Display(head): current = head # if list is empty, simply show messageif (head == None): print("\nDisplay List is empty\n")return # traverse first to last nodeelse: while(True): print( current.data,end=" ")current = current.nextif (current == head):break; # Function return number of nodes present in listdef Length(head):current = headcount = 0 # if list is empty # simply return length zeroif (head == None): return 0 # traverse first to last nodeelse: while(True): current = current.nextcount = count + 1if (current == head):break; return count # Function delete First node of# Circular Linked Listdef DeleteFirst(head):previous = headnext = head # check list have any node# if not then returnif (head == None) : print("\nList is empty")return None # check list have single node# if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous) : head = Nonereturn None # traverse second to firstwhile (previous.next != head):previous = previous.nextnext = previous.next # now previous is last node and# next is first node of list# first node(next) link address# put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = next.next # make second node as head nodehead = previous.next return head # Function to delete last node of# Circular Linked Listdef DeleteLast(head):current = headtemp = headprevious = None # check if list doesn't have any node# if not then returnif (head == None):print("\nList is empty")return None # check if list have single node# if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current) :head = Nonereturn None # move first node to last# previouswhile (current.next != head):previous = currentcurrent = current.next previous.next = current.nexthead = previous.next return head # Function delete node at a given position# of Circular Linked Listdef DeleteAtPosition(head, index): # Find length of listlen = Length(head)count = 1previous = headnext = head # check list have any node# if not then returnif (head == None):print("\nDelete Last List is empty")return None # given index is in list or notif (index >= len or index < 0) :print("\nIndex is not Found")return None # delete first nodeif (index == 0) :head = DeleteFirst(head)return head # traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0): # if index found delete that nodeif (index == count):previous.next = next.next return head previous = previous.nextnext = previous.nextlen = len - 1count = count + 1 return head # Driver Code head = Nonehead = Insert(head, 99)head = Insert(head, 11)head = Insert(head, 22)head = Insert(head, 33)head = Insert(head, 44)head = Insert(head, 55)head = Insert(head, 66) # Deleting Node at positionprint("Initial List: ")Display(head)print("\nAfter Deleting node at index 4: ")head = DeleteAtPosition(head, 4)Display(head) # Deleting first Nodeprint("\n\nInitial List: ")Display(head)print("\nAfter Deleting first node: ")head = DeleteFirst(head)Display(head) # Deleting last Nodeprint("\n\nInitial List: ")Display(head)print("\nAfter Deleting last node: ")head = DeleteLast(head)Display(head) # This code is contributed by Arnab Kundu |
| — |
C#
| // C# program to delete node at different // positions from a circular linked list using System; class GFG { // structure for a node class Node { public int data; public Node next; }; // Function to insert a node at the end of // a Circular linked list static Node Insert(Node head, int data) { Node current = head; // Create a new node Node newNode = new Node(); // check node is created or not if (newNode == null) { Console.Write("\nMemory Error\n"); return null; } // insert data into newly created node newNode.data = data; // check list is empty // if not have any node then // make first node it if (head == null) { newNode.next = newNode; head = newNode; return head; } // if list have already some node else{ // move first node to last node while (current.next != head) { current = current.next; } // put first or head node address // in new node link newNode.next = head; // put new node address into last // node link(next) current.next = newNode; } return head; } // Function print data of list static void Display( Node head) { Node current = head; // if list is empty, simply show message if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nDisplay List is empty\n"); return; } // traverse first to last node else{ do{ Console.Write("{0} ", current.data); current = current.next; } while (current != head); } } // Function return number of nodes present in list static int Length(Node head) { Node current = head; int count = 0; // if list is empty // simply return length zero if (head == null) { return 0; } // traverse first to last node else{ do{ current = current.next; count++; } while (current != head); } return count; } // Function delete First node of // Circular Linked List static Node DeleteFirst(Node head) { Node previous = head, next = head; // check list have any node // if not then return if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nList is empty\n"); return null; } // check list have single node // if yes then delete it and return if (previous.next == previous) { head = null; return null; } // traverse second to first while (previous.next != head) { previous = previous.next; next = previous.next; } // now previous is last node and // next is first node of list // first node(next) link address // put in last node(previous) link previous.next = next.next; // make second node as head node head = previous.next; return head; } // Function to delete last node of // Circular Linked List static Node DeleteLast(Node head) { Node current = head, temp = head, previous = null; // check if list doesn't have any node // if not then return if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nList is empty\n"); return null; } // check if list have single node // if yes then delete it and return if (current.next == current) { head = null; return null; } // move first node to last // previous while (current.next != head) { previous = current; current = current.next; } previous.next = current.next; head = previous.next; return head; } // Function delete node at a given position // of Circular Linked List static Node DeleteAtPosition( Node head, int index) { // Find length of list int len = Length(head); int count = 1; Node previous = head, next = head; // check list have any node // if not then return if (head == null) { Console.Write("\nDelete Last List is empty\n"); return null; } // given index is in list or not if (index >= len || index < 0) { Console.Write("\nIndex is not Found\n"); return null; } // delete first node if (index == 0) { head = DeleteFirst(head); return head; } // traverse first to last node while (len > 0) { // if index found delete that node if (index == count) { previous.next = next.next; return head; } previous = previous.next; next = previous.next; len--; count++; } return head; } // Driver Code public static void Main(String []args) { Node head = null; head = Insert(head, 99); head = Insert(head, 11); head = Insert(head, 22); head = Insert(head, 33); head = Insert(head, 44); head = Insert(head, 55); head = Insert(head, 66); // Deleting Node at position Console.Write("Initial List: "); Display(head); Console.Write("\nAfter Deleting node at index 4: "); head = DeleteAtPosition(head, 4); Display(head); // Deleting first Node Console.Write("\n\nInitial List: "); Display(head); Console.Write("\nAfter Deleting first node: "); head = DeleteFirst(head); Display(head); // Deleting last Node Console.Write("\n\nInitial List: "); Display(head); Console.Write("\nAfter Deleting last node: "); head = DeleteLast(head); Display(head); } } // This code is contributed by Rajput-Ji |
| — |
Javascript
| <script> // JavaScript program to delete node at different// positions from a circular linked list // A linked list nodeclass Node{constructor(new_data){this.data = new_data this.next = nullthis.prev = null}} // Function to insert a node at the end of// a Circular linked listfunction Insert(head, data){ let current = head // Create a new nodelet newNode = new Node(0) // check node is created or notif (newNode == null){ document.write("</br>","Memory Error","</br>")return null} // insert data into newly created nodenewNode.data = data // check list is empty// if not have any node then// make first node itif (head == null){newNode.next = newNodehead = newNodereturn head} // if list have already some nodeelse{ // move first node to last nodewhile (current.next != head) current = current.next // put first or head node address// in new node linknewNode.next = head // put new node address into last// node link(next)current.next = newNode} return head} // Function document.write data of listfunction Display(head){ let current = head // if list is empty, simply show messageif (head == null){ document.write("</br>","Display List is empty","</br>")return} // traverse first to last nodeelse{ while(true){ document.write( current.data," ")current = current.nextif (current == head)break;}}} // Function return number of nodes present in listfunction Length(head){let current = headlet count = 0 // if list is empty // simply return length zeroif (head == null) return 0 // traverse first to last nodeelse{ while(true){ current = current.nextcount = count + 1if (current == head)break;} } return count} // Function delete First node of// Circular Linked Listfunction DeleteFirst(head){let previous = headlet next = head // check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){ document.write("</br>","List is empty")return null} // check list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (previous.next == previous){ head = nullreturn null} // traverse second to firstwhile (previous.next != head){previous = previous.nextnext = previous.next} // now previous is last node and// next is first node of list// first node(next) link address// put in last node(previous) linkprevious.next = next.next // make second node as head nodehead = previous.next return head} // Function to delete last node of// Circular Linked Listfunction DeleteLast(head){let current = headlet temp = headlet previous = null // check if list doesn't have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){document.write("</br>","List is empty")return null} // check if list have single node// if yes then delete it and returnif (current.next == current){head = nullreturn null} // move first node to last// previouswhile (current.next != head){previous = currentcurrent = current.next} previous.next = current.nexthead = previous.next return head} // Function delete node at a given position// of Circular Linked Listfunction DeleteAtPosition(head, index){ // Find length of listlen = Length(head)count = 1previous = headnext = head // check list have any node// if not then returnif (head == null){document.write("</br>","Delete Last List is empty")return null} // given index is in list or notif (index >= len || index < 0) {document.write("</br>","Index is not Found")return null} // delete first nodeif (index == 0){head = DeleteFirst(head)return head} // traverse first to last nodewhile (len > 0){ // if index found delete that nodeif (index == count){previous.next = next.next return head} previous = previous.nextnext = previous.nextlen = len - 1count = count + 1}return head} // Driver Code let head = nullhead = Insert(head, 99)head = Insert(head, 11)head = Insert(head, 22)head = Insert(head, 33)head = Insert(head, 44)head = Insert(head, 55)head = Insert(head, 66) // Deleting Node at positiondocument.write("Initial List: ")Display(head)document.write("</br>","After Deleting node at index 4: ")head = DeleteAtPosition(head, 4)Display(head) // Deleting first Nodedocument.write("</br>","</br>","Initial List: ")Display(head)document.write("</br>","After Deleting first node: ")head = DeleteFirst(head)Display(head) // Deleting last Nodedocument.write("</br>","</br>","Initial List: ")Display(head)document.write("</br>","After Deleting last node: ")head = DeleteLast(head)Display(head) // This code is contributed by shinjanpatra </script> |
| — |
Output
Initial List: 99 11 22 33 44 55 66
After Deleting node at index 4: 99 11 22 33 55 66
Initial List: 99 11 22 33 55 66
After Deleting first node: 11 22 33 55 66
Initial List: 11 22 33 55 66
After Deleting last node: 11 22 33 55
Time Complexity: O(N) where N is the number of nodes in given linked list.
Auxiliary Space: O(1)